Journal of Daylighting
Journal of Daylighting is a peer-reviewed international journal devoted to investigations of daylighting in buildings. It is the leading journal that publishes original research on all aspects of Energy, buildings, and lighting. Read more
Open Access — free for readers, articles are published free-of-cost.
Rapid Publication: Bi-annual (articles are published continuously throughout the year)
Publication Fee: No charges
Year Started: 2014
Time to Publication: 70 days
Abstracting & Indexing
Scopus (Elsevier)
EBSCO
Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ)
Architectural Periodicals Avery Index
CrossRef

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Tessellation-Based Origami-Inspired Movable Façade for Daylighting and
This study emphasizes the importance of daylight performance in interior spaces as a critical factor in achieving global Sustainable Development Goals, including energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and healthy living conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 252-264

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Sensitivity Analysis and Optimization of Facade Design to Improve Daylight
This study examines the daylighting performance of a classroom with bilateral opening typology and an adjacent building on one side. The openings are located on the east and west sides of the classroom, with the adjacent building situated on the west side.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 235-251

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Integrating Acoustic Comfort and Daylighting in Transparent Multi-Purpose Halls:
Multi-purpose halls are halls where many different activities, such as music, theater, speech, and shows, can be performed in the same space. Recently, multi-purpose halls illuminated with daylight have been frequently seen.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 215-234

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Assessing the Indoor Thermal Comfort and Adaptive Behaviours of Older
Population aging, extreme weather conditions, and rising energy costs present significant challenges, especially in developing Asian countries like India.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 190-214

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Balancing the Parameters of Perforated Solar Screens to Optimize Daylight
Perforated solar screens (PSSs) have been widely used as an outer skin for the fully glazed façades of office buildings for their environmental and aesthetic benefits..
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 167-189

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Framework for Integrating Zoning Regulations and Site Layout Design
Daylight is one of the primary sources to ensure a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient neighborhoods. Zoning regulations significantly influence daylight-driven site layouts by constraining design decisions, particularly at the neighborhood scale.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 148-166

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analyses of Switchable Slat Insulated Shades for
To balanced multi-criteria's daylighting performance in indoor spaces, several dynamic metrics have been proposed, but so far there is no convention on which daylight metrics thresholds are preferred and which objective weights are given priority in optimization of daylighting under certain climate.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 125-147
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-Objective Performance Evaluation Framework for Integrated Fiber-Reinforced Shading
Shading systems are associated by their ability to control various factors such as energy consumption, visual comfort, and natural ventilation. To fulfill such economic, environmental, and social requirements, the use of integrated modular fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) shading systems has become popular in recent years.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 111-124
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-objective Optimization of Window and Shading Systems for Enhanced
Addressing the challenges of global warming and rising energy demands, this study explores fixed shading systems as passive and sustainable solutions to improve energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and daylight performance in office buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 91-110

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Designing Adaptability Strategy to a Novel Kinetic Adaptive Façade (
The design and evaluation of adaptive facades (AFs) have become increasingly complex due to advancements in morphology, control strategies, and adaptability techniques.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 69-90

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Feasibility Study of Five Solar Thermal Power Plants in Arequipa,
Knowing the Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) allows for evaluating the profitability of different energy generation technologies, identifying the options with the lowest costs, and, in turn, promoting the transition to more sustainable energy sources for governments and private companies.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 51-68

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimisation of Indoor Spatial and Temporal Aspects of Deep Architectural
Visual comfort in deep rooms with side lit openings varies by positions and time; thus, interventions are required to provide comfort for all users in a room.
Journal of Daylighting (2025) 40-50

RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Curved Light Shelves, Ceiling and Window Characteristics
Daylighting is related to the user's psychological and physiological effects in educational space. The amount of daylighting significantly influences visual comfort, work tasks, academic performance and productivity.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 21-39

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Optimization of the South-Faced Architecture Classrooms Using Biomimicry-
Building design is a product of multiple factors, such as concept and aesthetics, building materials and technologies, environmental conditions, and daylight requirements of the inner spaces.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 1-20
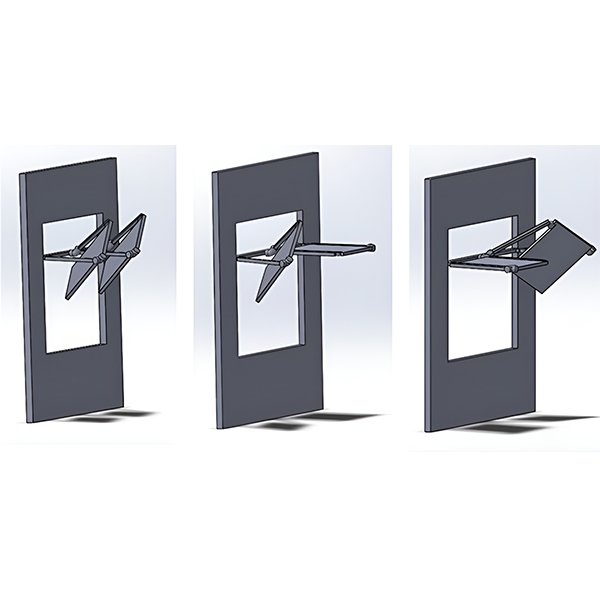

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Alternatives of Light Shelves using Altmann Linkage
This paper proposes a novel new light shelf design with Altmann linkage using its kinetic principles: geometry and rotational angles. As previous studies explain a light shelf’s design in two ways: static and movable, the proposed one in this study has the potential to track the path of the sun due to its diagonal movement. .
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 391-407
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Unfolding 3D Space into Binary Images for Daylight Simulation via
Daylighting plays a crucial role in building science, impacting both occupants’ well-being and energy consumption in buildings. Balancing the size of openings with energy efficiency has long been a challenge. .
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 204-2013
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Integrative Lighting Design: How to Optimize Visual and Non-visual
The objective of this paper is to outline fundamental principles for the electric lighting design of workplace environments such as offices. The study considers both the suggested guidelines and values for non-visual light design and the specifications for visual tasks dictated by the EN 12464-1:2021.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 192-203
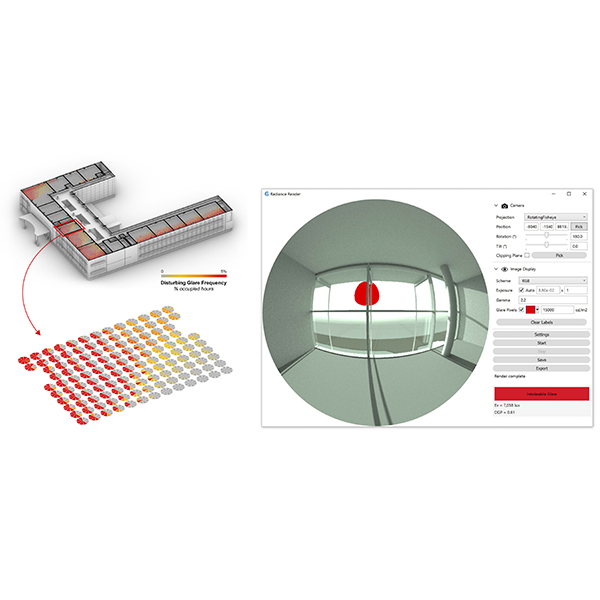
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Parametric Patterned Façade Variations on Daylight
Parametric design influences on building envelope design are exponentially increasing in the current era due to the dominance of computational design on architectural outcomes.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 173-191
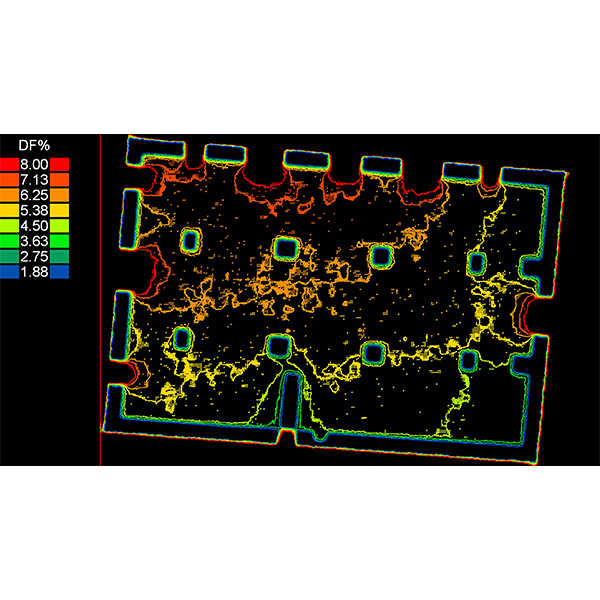
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analysing the Daylighting Performance of the Main Prayer-hall in
This paper studies the daylighting quality of the indoor prayer-hall in The Great Upper Mosque of Hama city in Syria, highlighting this distinctive historical converted building that has been functioning as a mosque since the entry of Islam in the 6th century AD.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 153-172
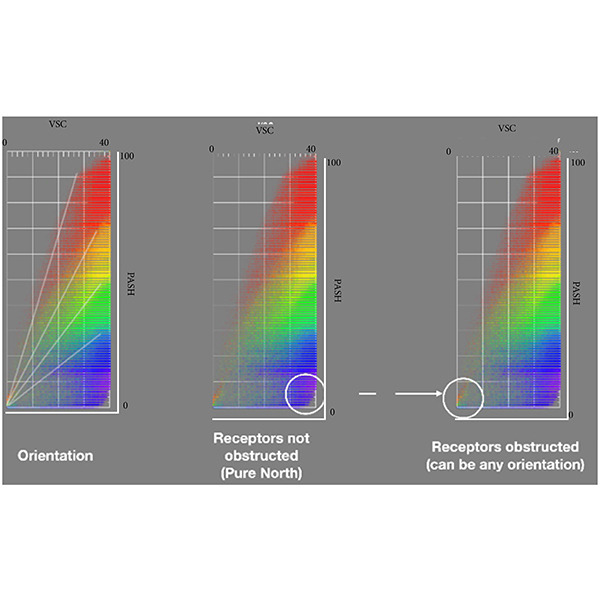
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Sunlight-Daylight Signature: a Novel Concept to Assess Sunlight and
Daylighting and solar availability at urban scale has come to play a crucial role in the perception of discomfort conditions for people, both in outdoor and indoor spaces, and on the energy consumption of buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 136-152
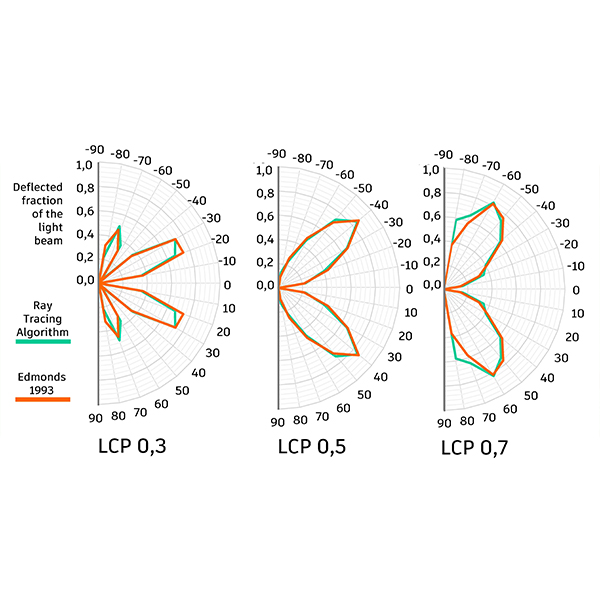
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Ray Tracing Algorithm to Simulate Laser-Cut Panel Light-Redirecting
Daylighting simulation software is an important tool to improve the quality of building design and to improve the quality of the built environment. For its application to correspond to reality, its algorithm needs to reflect real behaviour in the best possible way.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 87-98
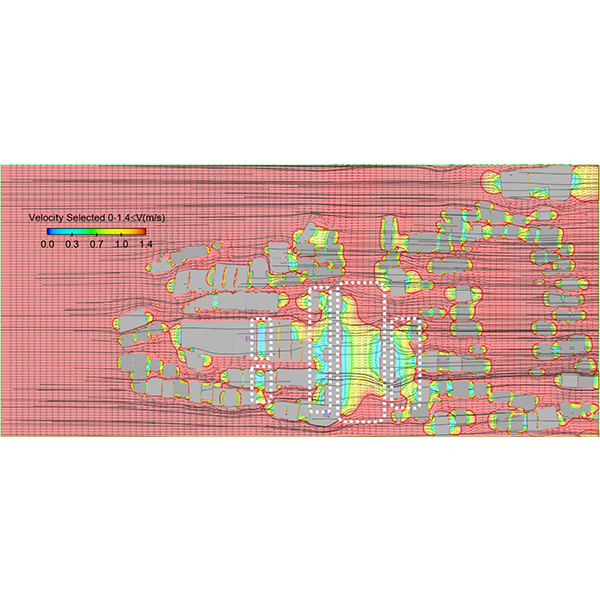
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effects of Orientation and Width of Space Between Buildings
Excessive heat in the high-rise urban fabric has contributed to pedestrian and occupants' discomfort. Establishing wind circulation in space with an environmentally compatible and optimal configuration is necessary to improve comfort in this region.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 99-116
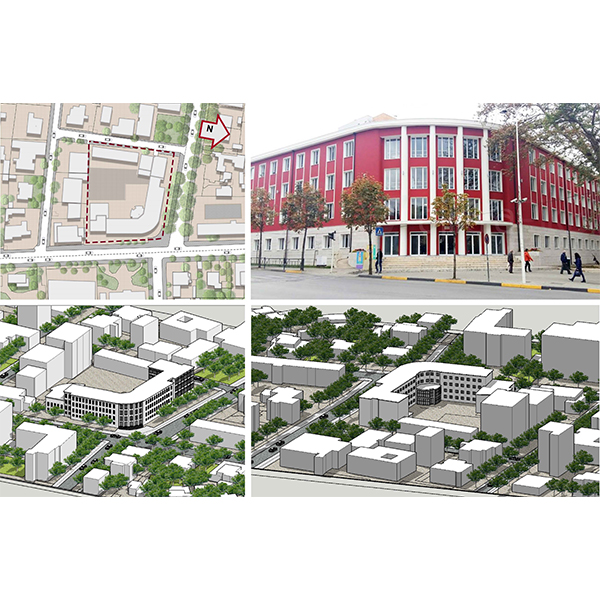

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of the Visual Comfort and Daylight Performance of the
The daylight in classrooms is a crucial aspect that affects the quality of the learning environment and the overall performance of the students. Visual arts, such as painting, sculpture, carving, textile design and photography, require specific lighting conditions, which are different from the regular classroom standards.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 117-135
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Optimization of the Skylight for Daylighting and Energy Performance
In terms of sustainable design, lateral windows and skylights are important. Daylighting has become a vital component in office buildings because it increases occupants' productivity, well-being, and energy savings via windows and skylights.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 72-86

RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Architectural Design of Building Façade Models Related to
Lighting control integrated with daylighting is recognized as an important and useful strategy in energy efficient building design. One of the right factors to reduce energy consumption for artificial lighting during the day is the maximum utilization of sunlight.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 60-71

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of Occupants’ Visual Perception in Day Lit Scenes: A
Daylight improves indoor environmental quality, the physical and mental health of occupants, and their efficiency. Research in the area of human-centric lighting that considers the visual and non-visual effects of light on human vision, have focused on examining human visual perception in response to a wide variety of lighting aspects.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 45-59

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Impact of Window Design on Dynamic Daylight Performance in an
Window design affects the building's appearance. Besides, it has a significant impact on daylight performance and the visual comfort of interior spaces.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 31-44

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Visual Comfort Assessment of Hospital Patient Rooms with Climate Responsive
As advanced technologies become prevalent, they are being used more widely in numerous fields. The building sector is not an exception. One of these cutting-edge technologies is responsive facades, which are used in buildings and have an undeniable effect on daylighting.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 17-30

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Biomimicry as an Approach to Improve Daylighting Performance in Office
Biomimicry inspired architects to solve complex design problems and develop adaptive solutions for enhancing the environmental quality. Fields of inspiration include energy efficiency, natural ventilation, daylighting, and structural stability.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 1-16
Join our Editorial Board
Applications should be sent electronically at jd@solarlits.com.
Editorial Board

Prof. Önder Güler
Istanbul Technical University, Türkiye

Prof Hongfei Zheng
Beijing Institute of Technology, China

Dr Boon Han Lim
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia

Dr Arsenio Barbón
University of Oviedo, Spain

Prof Laura Bellia
University of Naples Federico II, Italy

Prof. Yuehong Su
University of Nottingham, UK

Dr Susana Lagüela López
University of Vigo, Spain

Dr Ferdinando Salata
University of Rome, Italy

Prof. Barbara Szybinska Matusiak
NTNU, Norway

Dr Fabio Peron
IUAV University of Venice, Italy

Prof Francesco Asdrubali
University of Perugia, Italy

Prof. Lambros T. Doulos
Hellenic Open University, Greece

Dr Guiqiang Li
University of Science and Technology of China, China

Dr Umberto Berardi
Ryerson University, canada

Dr. Kacem Gairaa
center for renewable energy development, Algeria

Dr Lim Yaik Wah
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia

Dr Mohammed Salah Mayhoub
Al-Azhar University, Egypt

Dr Osama Mohamed Omar
University of Bahrain , Bahrain

Dr Rizki A. Mangkuto
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia

Wei Wang
Southeast University, 中国

Prof. BANU MANAV
Kadir Has University, Turkey

Dr Hui Shen
Texas A&M University-Kingsville, USA

Dr Doris Abigail Chi Pool
Universidad de las Américas Puebla, Mexico

Prof Jitka Mohelnikova
Brno University of Technology, Czech Republic

Dr jian yao
Ningbo University, China

Dr Paula M. Esquivias
University of Granada, Spain

Omid Nematollahi
Isfahan University of Technology, South Korea

Dr. Peng XUE
Beijing University of Technology, China

Dr. Francesco Nocera
Department of Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of Catania (ITALY), Italy

Dr Vincenzo Costanzo
University of Catania, Italy
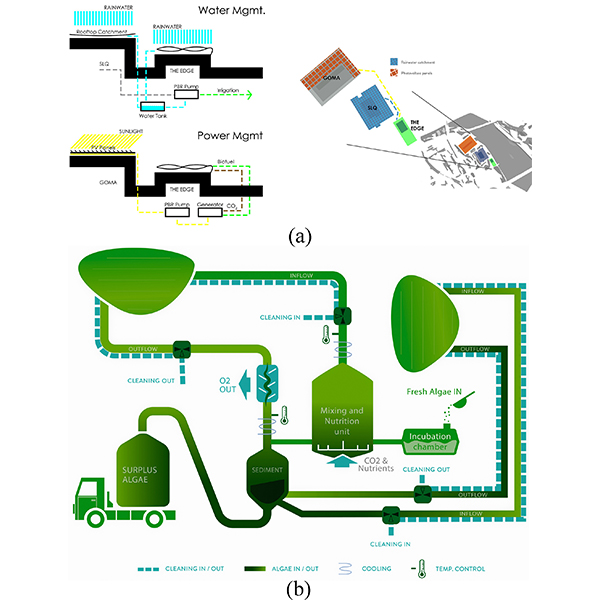
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Photobioreactors as a Dynamic Shading System Conceived for an Outdoor
In the field of responsive shading systems, the use of photobioreactors (PBRs) containing microalgae seems to be a promising technology. Within this framework, this paper presents a case study where a PBR was specifically conceived as a shading system for an external workspace located on an open terrace of the State Library of Queensland (SLQ) in Brisbane.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 148-168

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Quantitative Investigation Through Climate-based Daylight Metrics of Visual Comfort
There are several alternatives to passive strategies in the early stages of the design process including orientation, window to wall ratio, shading device, material and colour that affect occupants’ visual comfort. .
Journal of Daylighting 5 (2018) 21-33
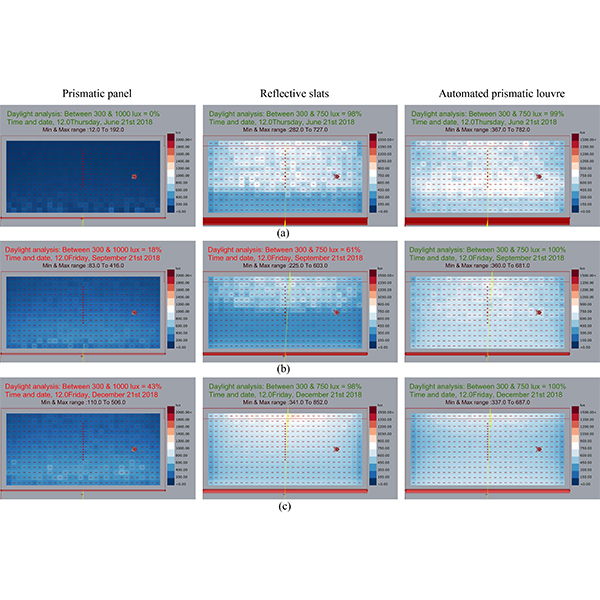
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Distribution Improvement Using Automated Prismatic Louvre
Louvre is a common type of shading devices and has been increasingly used in office buildings. Meanwhile, some reflective types of louvre have been used to provide shade and to redirect daylight deep into buildings interior simultaneously.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 84-92
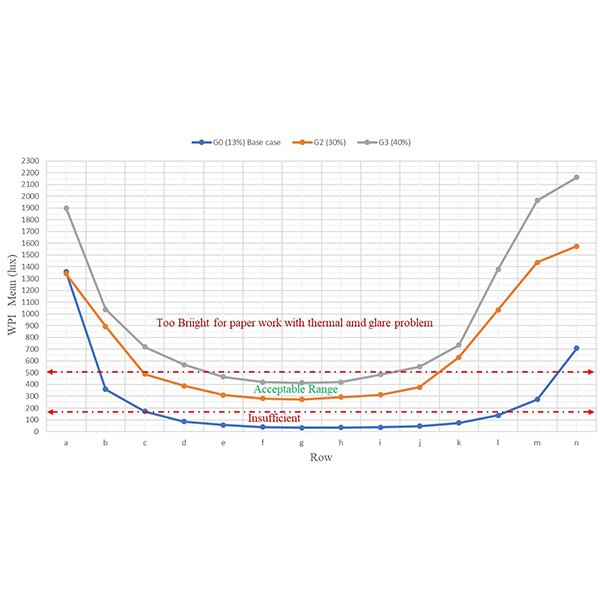
RESEARCH ARTICLE
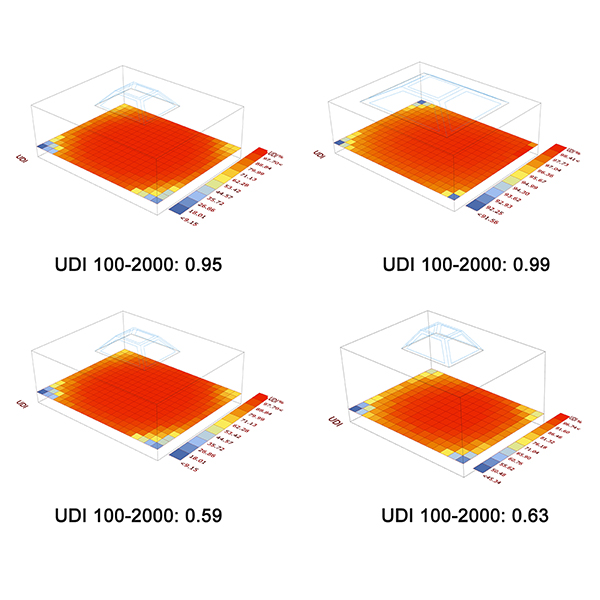
Daylighting Evaluation and Optimisation of Window to Wall Ratio for
A base case model is a more potent dose for applied research; the passive architectural design for sustainability requires optimised experiments. However, experimenting with physical developments require construction and deconstruction until they achieved the optimal scenario.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 20-35
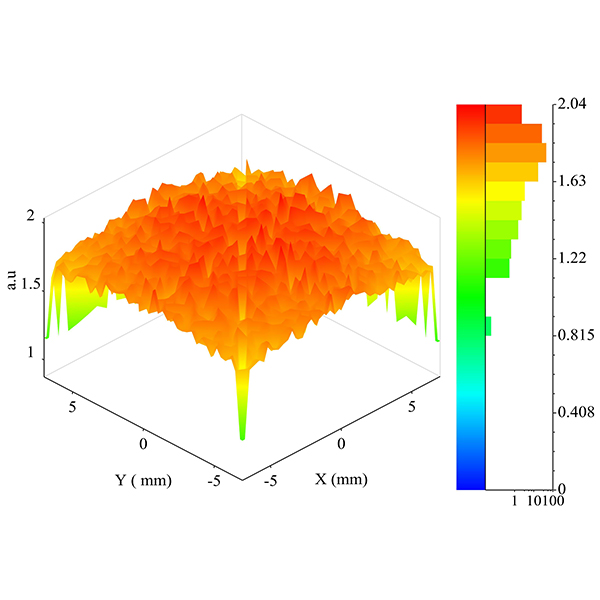
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of Fresnel-based Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) System with Uniform
Different designs have been presented to achieve high concentration and uniformity for the concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) system. Most of the designs have issues of low efficiency in terms of irradiance uniformity.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 2-7
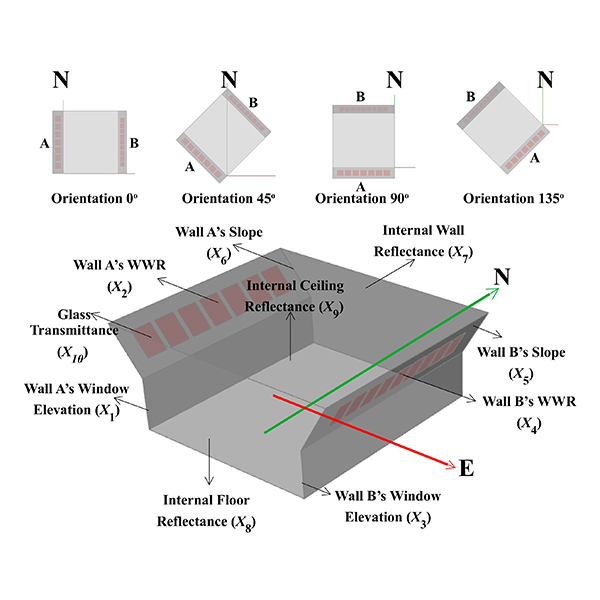
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimization of Daylighting Design Using Self-Shading Mechanism in Tropical
Despite its potential, daylighting strategies in school classrooms in the tropical climate regions is little explored in the literature. The use of two-sided or bilateral daylight opening, as well as the self-shading mechanism using sloped walls, are currently seen as potential strategies to achieve good daylighting in tropical buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 117-136
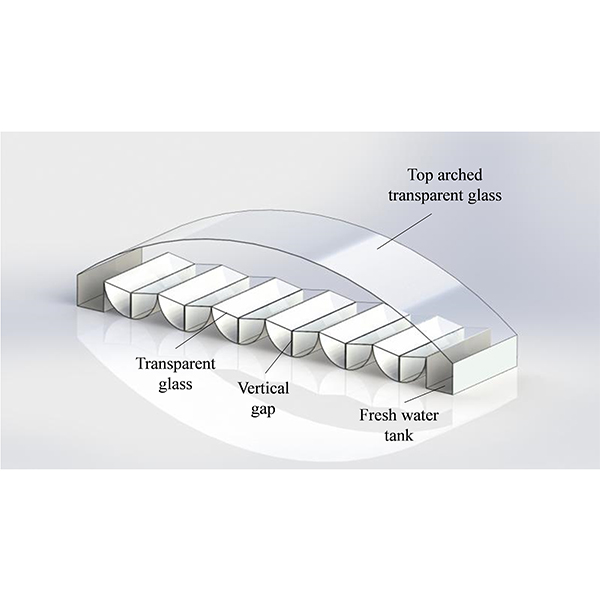
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optical Analysis of a New Solar Distiller with Cylindrical Surface
In this paper, a new solar distiller floating on ocean with cylindrical surface concentrator and vertical gap evaporator is proposed for solving the problem of freshwater shortage in islands.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 100-109
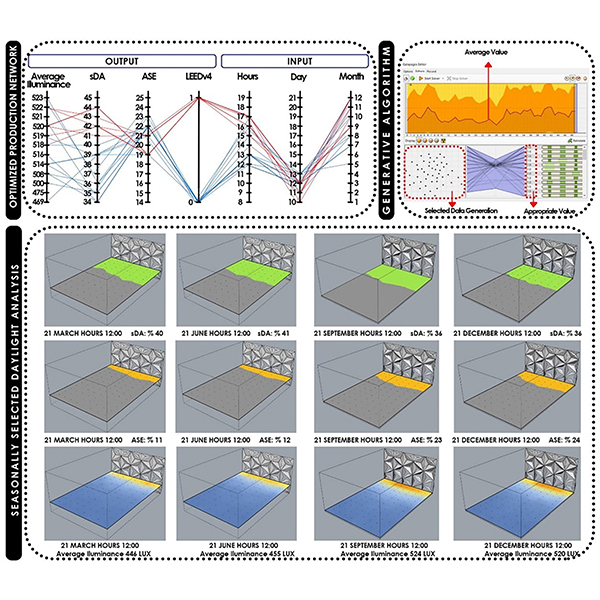
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of Daylight and Glare Quality of Office Spaces with
There has been an increasing awareness in recent years about the evaluation of daylight and glare quality in buildings. In the study, an office space with a flat and a dynamic shading system facade (triangular cell facade) is discussed in the province of Mardin, which is in a hot and arid climate zone.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 197-208
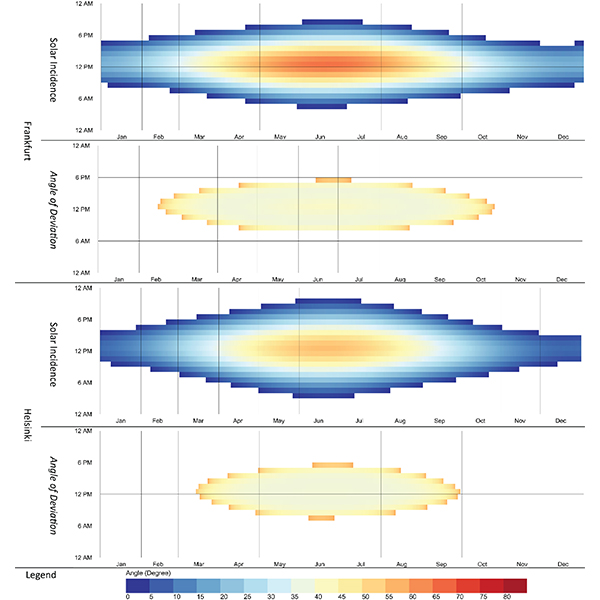
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Solar Angle Model for Daylight Redirection in Prismatic Panel
An advanced complex fenestration system can utilize uniform daylight. Nonetheless, an inefficient design would increase solar heat gain and indoor temperatures, besides uneven light distribution that would cause the "cave effect.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 257-265
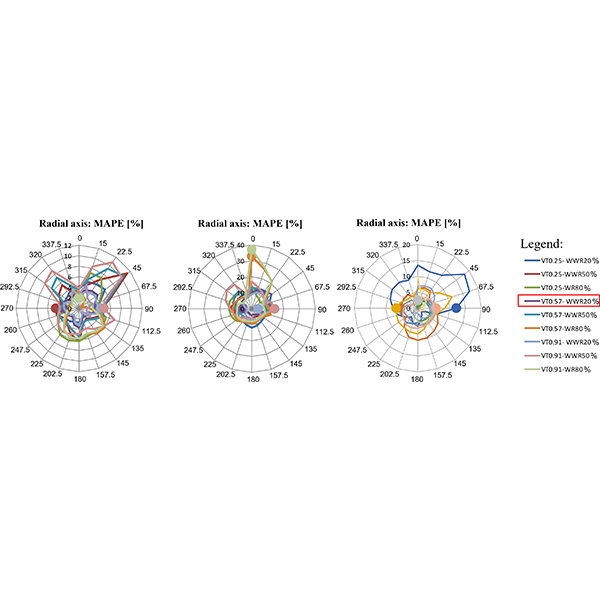
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Metamodeling of the Energy Consumption of Buildings with Daylight Harvesting –
Daylight harvesting is a well-known strategy to address building energy efficiency. However, few simplified tools can evaluate its dual impact on lighting and air conditioning energy consumption.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 255-269
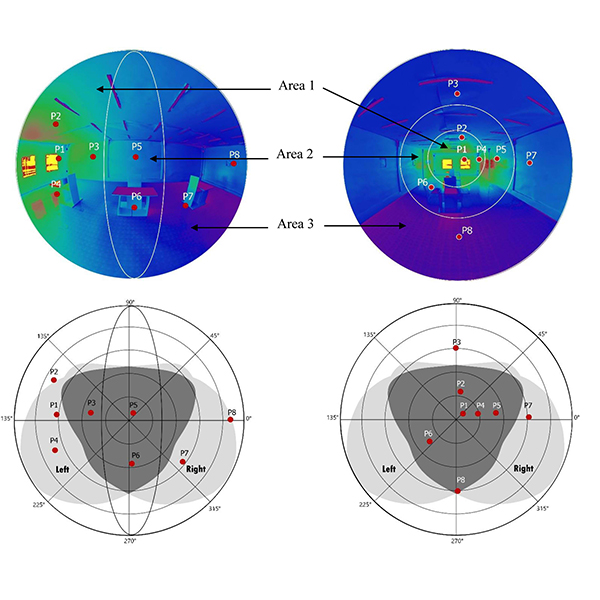
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Combined Method for an Exhaustive Investigation of the Anidolic
Lighting quality in office environments is a broad concept that must be taken into account in the design stage to deliver comfortable spaces to reduce workers' stress.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 149-164
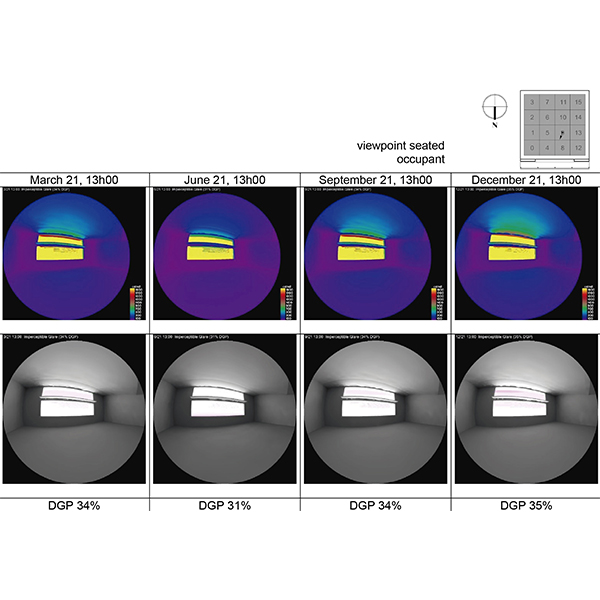
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimisation of Passive Solar Design Strategies in Side-lit Offices:
It has been shown that in buildings with fully glazed facades designed to save electricity and increase daylight, overheating due to excessive solar gains and glare have become recurrent problems, affecting the quality of the indoor environment in office buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 107-121
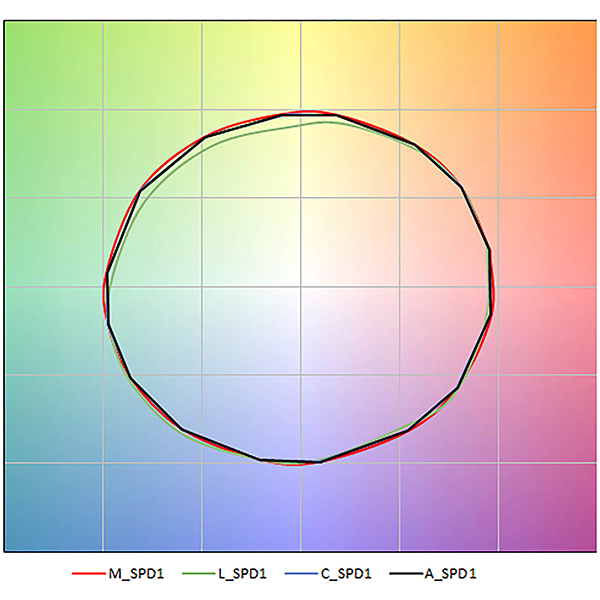
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Effect of window glazing on colour quality of transmitted daylight
In this study, the colour quality of the daylight transmitted through different window glazing types is evaluated. The analysis considered four different types of window glazing: laminated, monolithic, coated and applied film glazing ranging in luminous transmittance from around 0.
Journal of Daylighting 4 (2017) 37-47
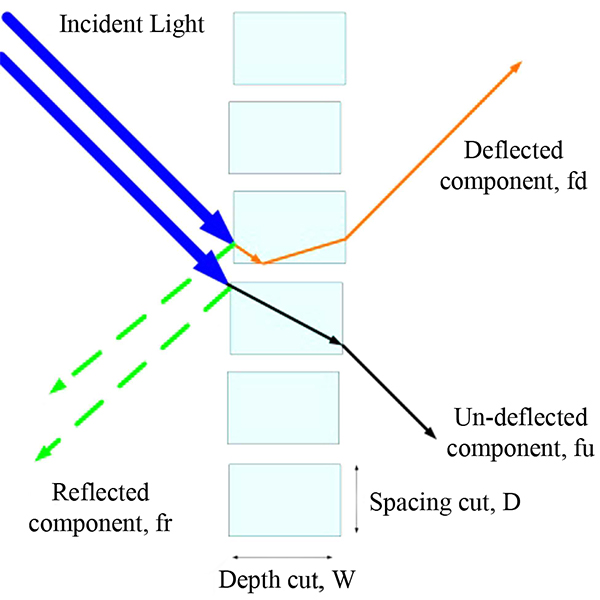
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Maximizing the Performance of Laser Cut Panel by Interaction of
The interaction between different ceiling geometries with laser cut panels (LCPs) is investigated using real experiments and computer simulations to maximize the daylight performance of the LCP.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 29-35
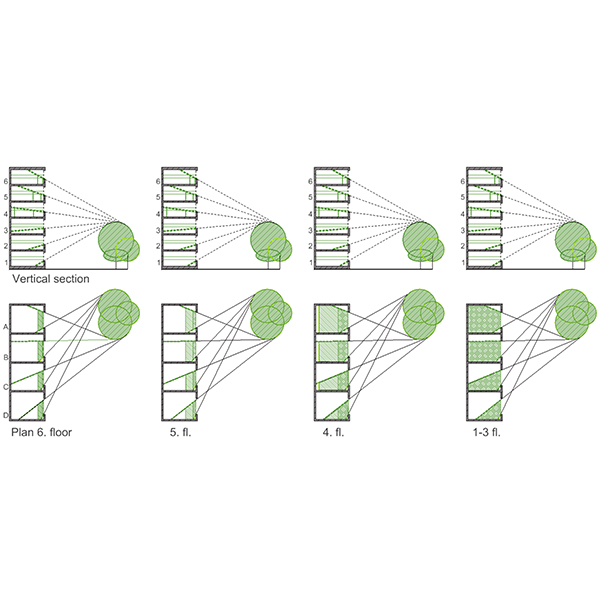
SHORT COMMUNICATION
No-Greenery Line and Greenery-View Factor, New Architectural Design
The paper proposes a new tool for evaluation of the degree of visual contact with the outdoor greenery, the Greenery-View factor (GV), intended to be easy to grasp and simple to use.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 282-286
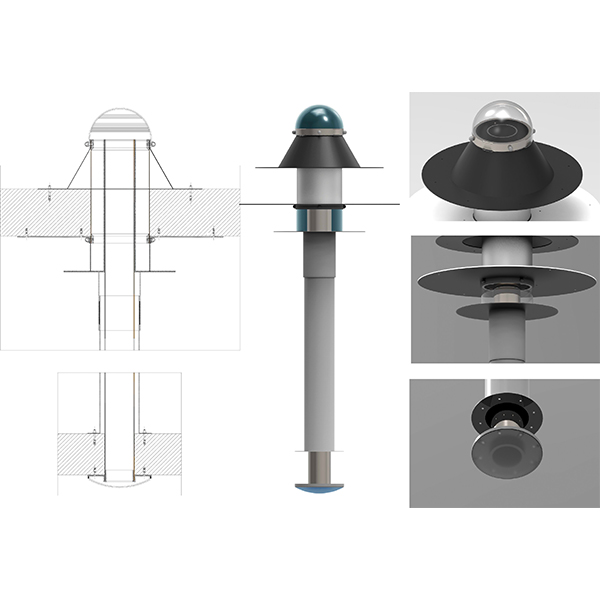
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Performance of the Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP) Through
This paper focuses on the Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP), an innovative daylighting system set up by the authors in the Laboratory of Technical Physics of the University “G. .
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 164-176
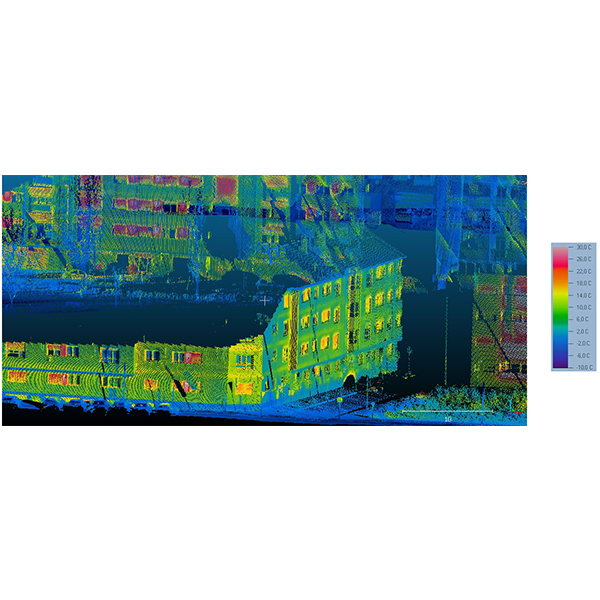
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Thermographic Mobile Mapping of Urban Environment for Lighting and Energy
The generation of 3D models of buildings has been proved as a useful procedure for multiple applications related to energy, from energy rehabilitation management to design of heating systems, analysis of solar contribution to both heating and lighting of buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 8-15
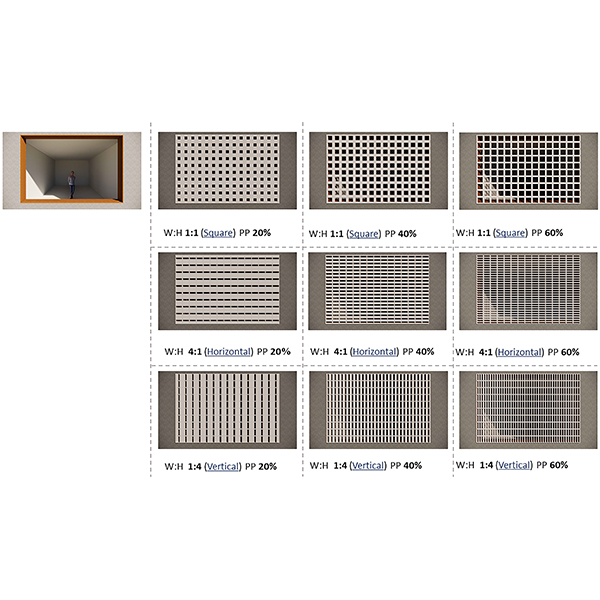
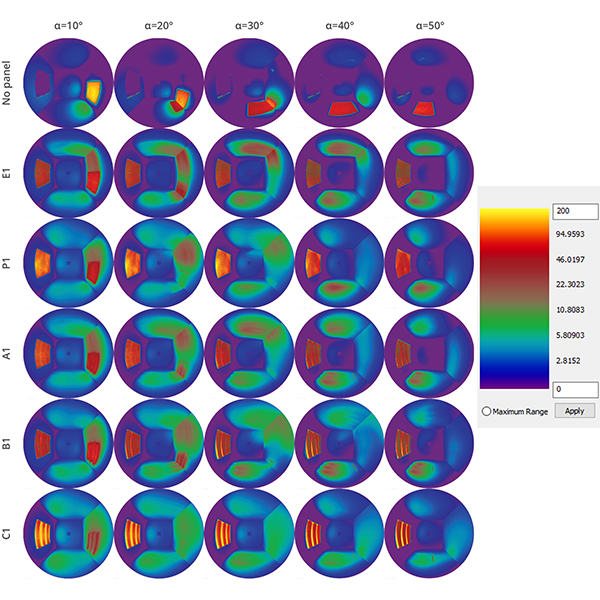
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Significance of Aperture Proportion for the Lighting Behaviour and
Traditional solar screens in Iran (called Moshabak) are architectural devices used mainly in hot-arid regions, with two interrelated functions: controlling the penetration of sunlight and gaze from outside.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 242-256
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Towards New Design of Laser Cut Acrylic Panels for Windows
This paper builds upon existing research into laser cut panels and aims to find new design-patterns that would improve daylighting conditions of existing rooms when applying the laser-cut panels on vertical windows.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 1-10
RESEARCH ARTICLE
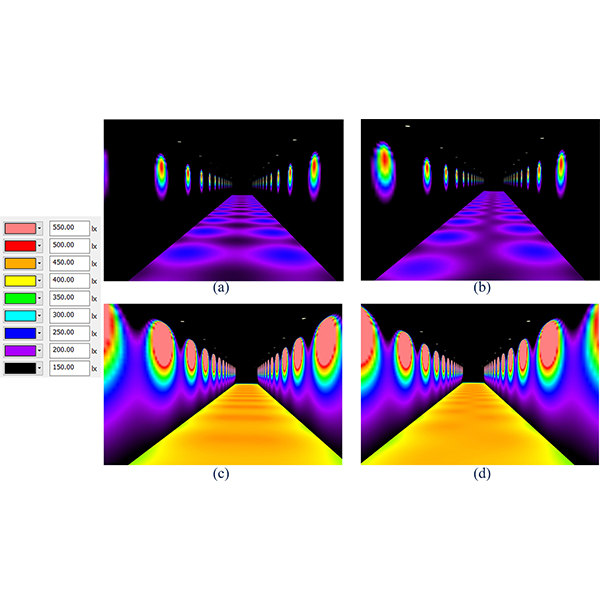
Phasor Method to Estimate Illuminances Due to Parallel Arrays of
Direct horizontal illuminance along a calculation row due to two parallel arrays of large numbers of identical light sources behaves like a periodic signal with a sinusoidal pattern, which contains useful information for design purpose.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 246-257
RESEARCH ARTICLE
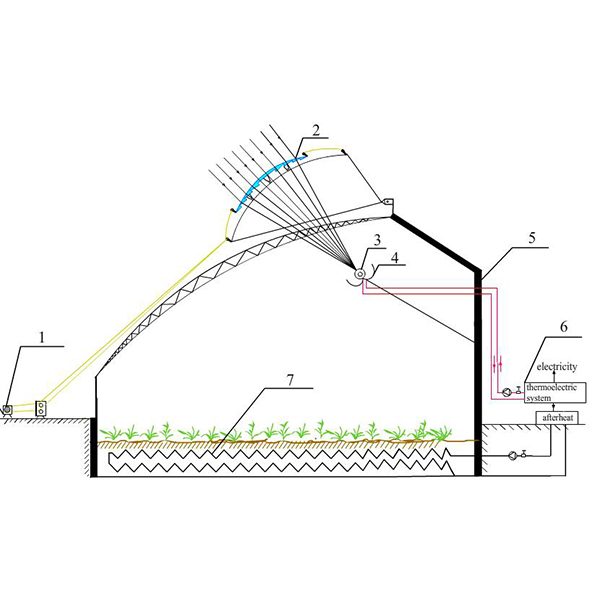
Optical Analysis of A Sliding-Type Cylindrical Fresnel Lens Concentrating
Agricultural greenhouses are commonly built around cities to supply residents with agricultural products or green plants. With an increasing demand for plants’ growing environment, the temperature and illumination inside the greenhouses are counted especially during cold winter. .
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 110-119
RESEARCH ARTICLE
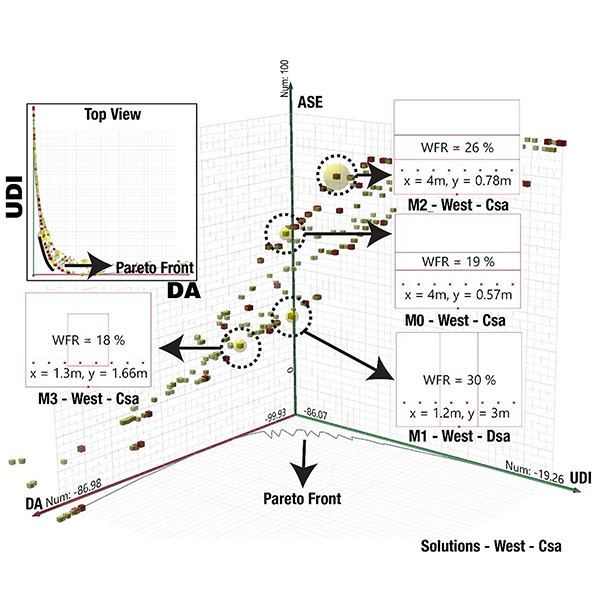
A Field-validated Multi-objective Optimization of the Shape and
This study aims to determine the optimum size of windows based on the window-to-floor ratio (WFR) for the main cardinal directions in Hot-summer Mediterranean (Csa) and Dry Summer Continental (Dsa) climates (Köppen–Geiger classification system) by carrying out a multi-objective optimization that relies on three dynamic metrics of Useful Daylight Illuminance (UDI-a (autonomous)), Daylight Autonomy (DA), and Annual Sunlight Exposure (ASE1000,250) in Radiance version 5.1..
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 222-237
RESEARCH ARTICLE
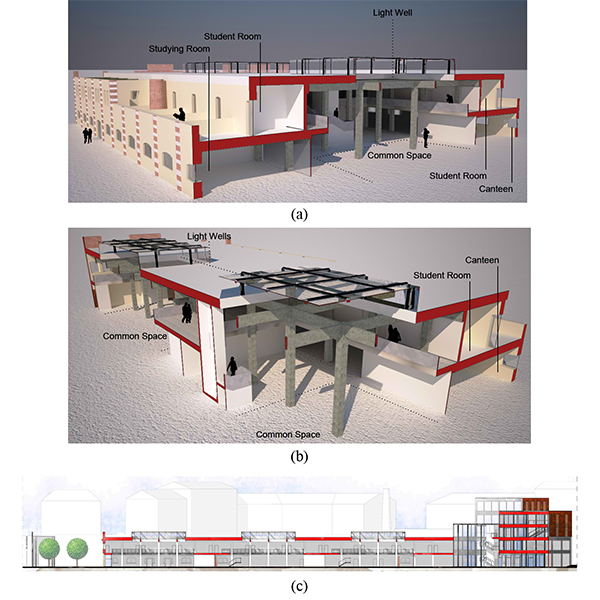
Daylighting as the Driving Force of the Design Process: from
This paper presents a study for the transformation of an industrial area in Turin, Italy. The area hosts two buildings (one of which appointed as listed) to be transformed into dwellings.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 36-55
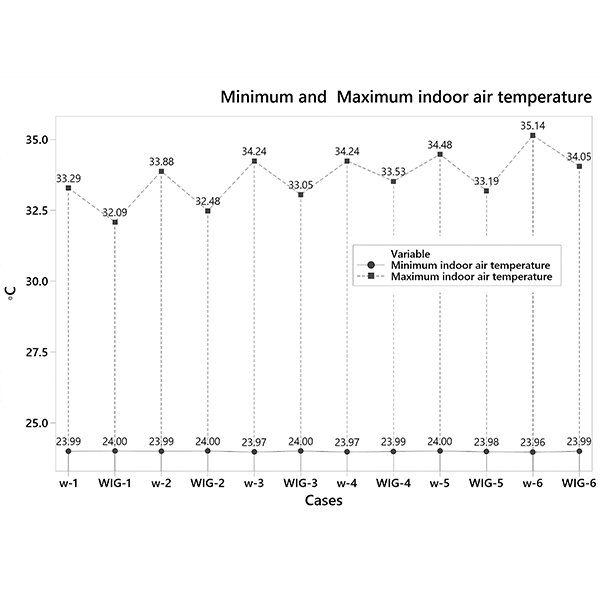
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Assessment of the Thermal Performance of Vertical Green Walls Using
Construction of multifunctional building envelopes using vertical greenery walls (VGW) has emerged as a sustainable green technology to improving cooling efficiency.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 294-312
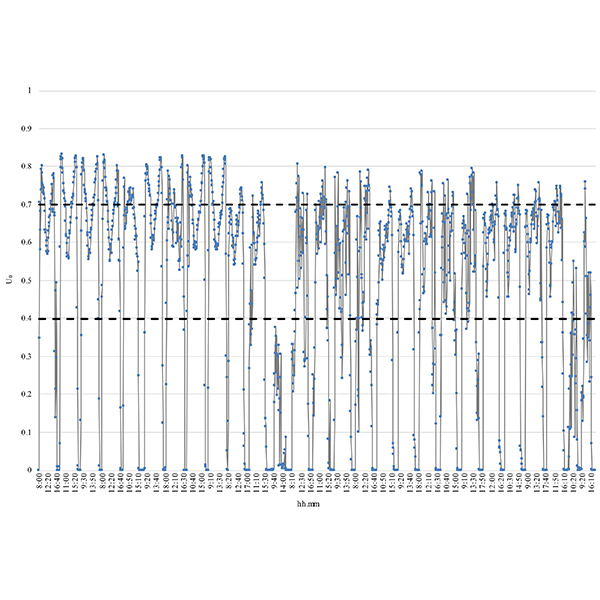
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental Analysis on a 1:2 Scale Model of the
This paper is focused on the daylighting system named Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP) designed by the authors as an evolution of the Double Light Pipe to eliminate the drawbacks due to its encumbrance and the high luminance of its upper portion.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 228-241
 HOME
HOME