Journal of Daylighting
An international journal devoted to investigations of daylighting in buildings. It is the leading journal that publishes original research on all aspects of Energy, buildings, and lighting.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Exploration of Natural Lighting and Visual Comfort in Contemporary
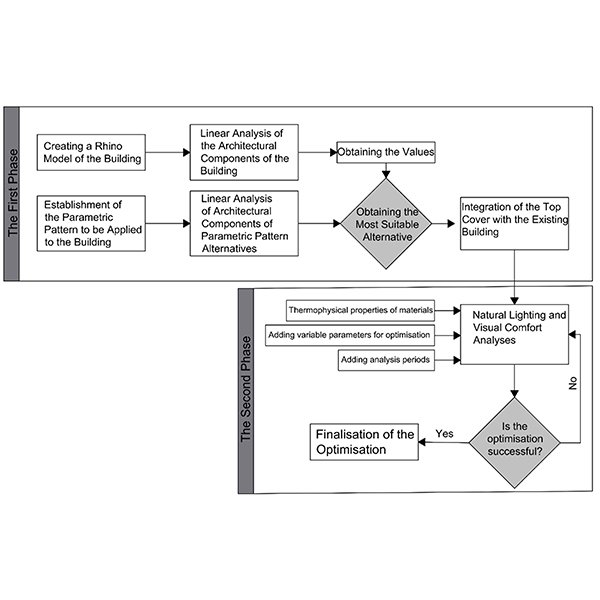
The re-functioning of historical buildings frequently necessitates new additions. This is particularly relevant for historical buildings with open courtyards, where interventions often involve the installation of upper covers using contemporary materials and techniques This issue can become especially apparent in historical buildings that are completely enclosed with transparent materials, raising concerns about the greenhouse effect and its potential to compromise indoor comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 506-519
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-Criteria Optimization of Tubular Daylighting Devices for Classrooms in
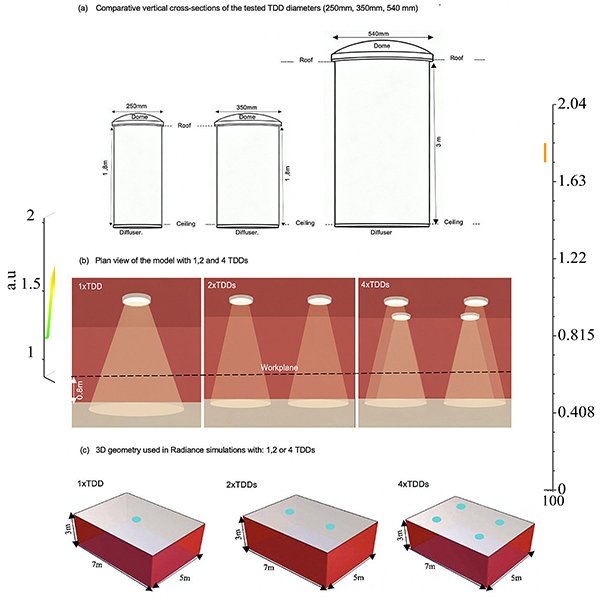
In educational architecture, particularly in high-solar climates, achieving a balance between ample daylight and visual comfort is a significant challenge.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 491-505
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-objective Optimization of Girih Tile Patterns and Colored Glass
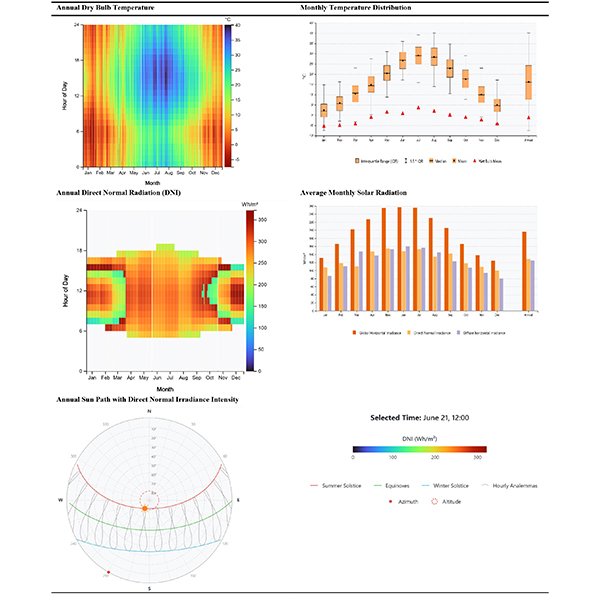
Efficient energy use is vital in architecture, and the building envelope plays a key role in aesthetics, thermal comfort, energy efficiency, and natural lighting.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 441-467
REVIEW ARTICLE
Human Interaction with Urban Morphology under the Influence of Urban
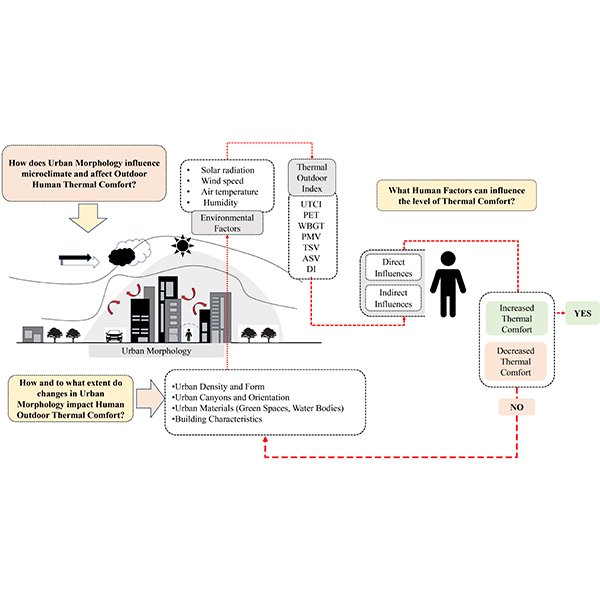
Outdoor urban spaces are essential to residents’ well-being, yet their thermal comfort is increasingly compromised by urbanization and climate change. .
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 468-490
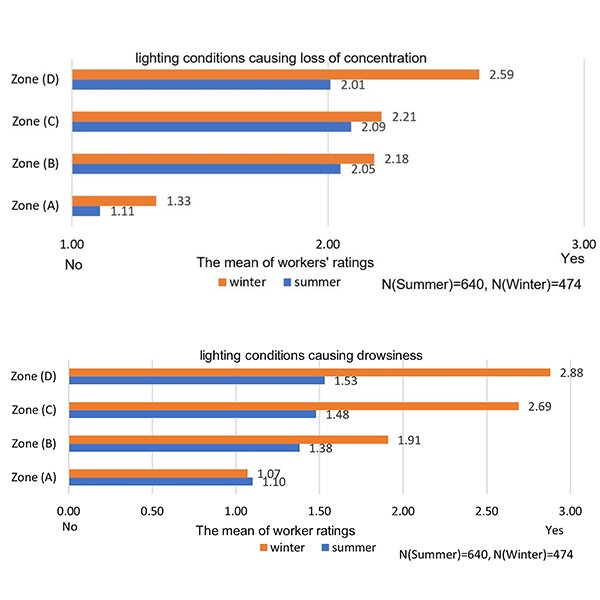
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating the Impact of Lighting Conditions on Workers’ Safety and
Lighting is a key element of design that plays a significant role in affecting workers’ health and safety in industrial workspaces. Given the scarcity of scientific studies addressing visual environments in relation to workers health in industrial buildings, this field study was conducted to explore workers' responses to multiple lighting scenarios inside production halls on their occupational health and safety in six factories in Sadat City, Egypt. .
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 420-440
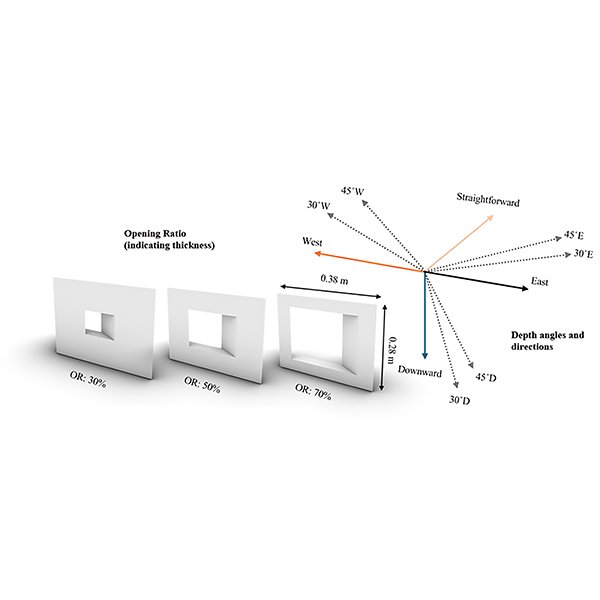
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating Daylighting Performance of Parametric Mashrabiya in Mediterranean Climate: A
This study examines the daylighting performance of parametric Mashrabiya-inspired shading devices in a Mediterranean climate, aiming to enhance occupant comfort and visual performance.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 397-419
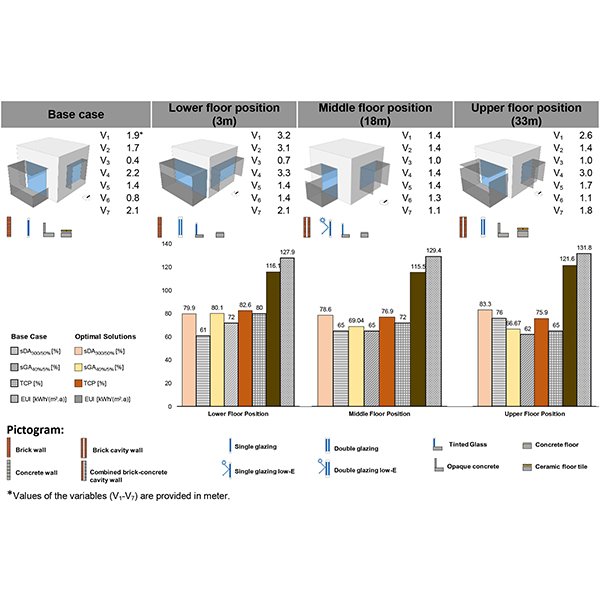
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Height-Responsive Balcony-Integrated Envelope Design for High-Rise Residential
Balconies function as essential shading elements within the building envelope, playing a critical role in regulating occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 375-396
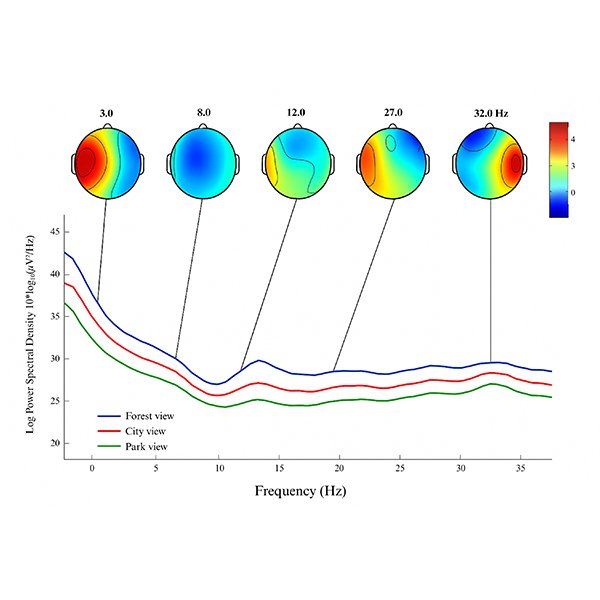
RESEARCH ARTICLE
EEG-Based Neurophysiological Responses to Classroom Window Views in Green
This study examines the neurophysiological responses of students to different classroom window views - forest, park, and city - within energy-efficient, green campus environments.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 359-374
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Enhancing Year-Round Thermal Comfort with Solar Control Films: A
Windows significantly contribute to thermal discomfort in high solar irradiance climates by allowing excessive heat gains and uneven indoor temperatures.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 343-358
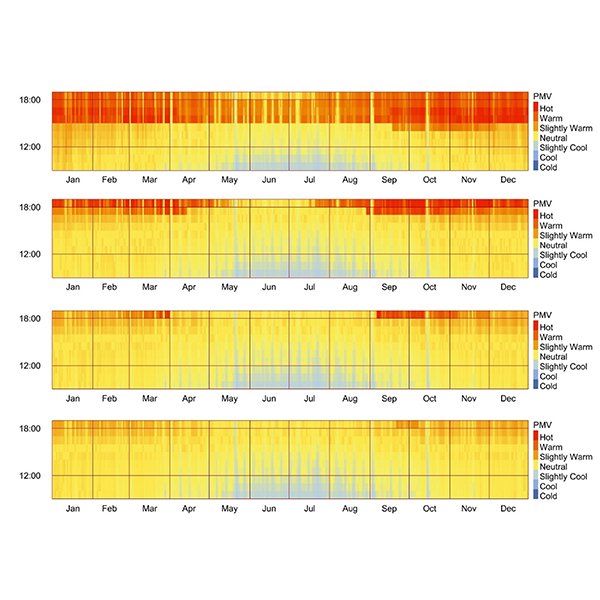
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating Visual and Beyond-Vision Light Effects and Energy Consumption
Light influences human physiology and psychology through visual and beyond-visual effects, collectively termed ‘integrative lighting.’ Human responses depend on luminous (quantity, spectrum, directionality) and temporal (timing, duration, history) factors, yet no studies examined their combined influence on integrative lighting. Th.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 306-342
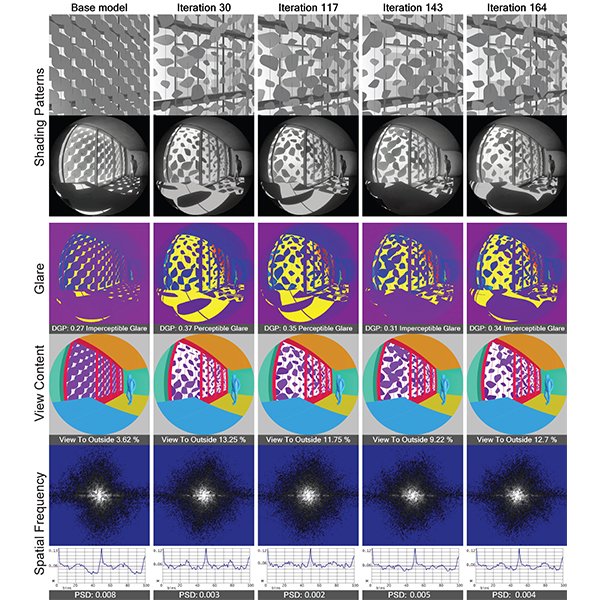
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Occupant-Centric Visual Comfort Assessment and Optimization of Passive Solar
This study introduces a comprehensive computational framework integrating image-based simulations, spatial frequency analysis, and multi-objective optimization to evaluate and optimize passive solar shading devices from an occupant-centric perspective.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 293-305
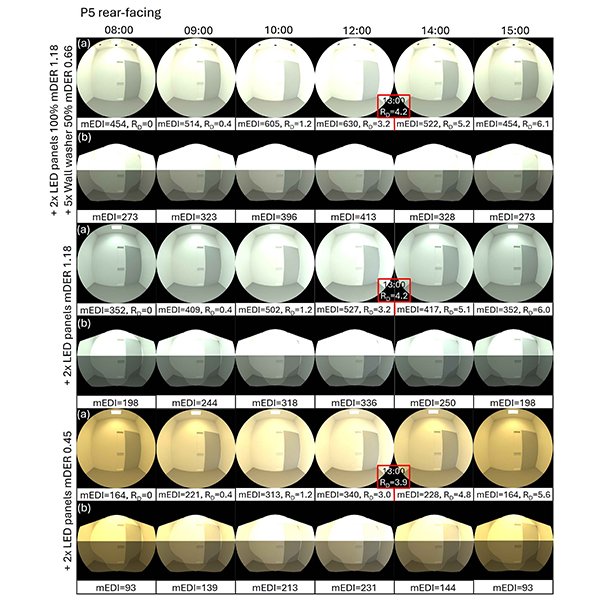
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Determination of Efficiency of the Vertical Specularly Reflecting Cylindrical Light
Article is devoted to determination of efficiency of the vertical specularly reflecting cylindrical light shaft for various types of the firmaments standardized by CIE (International Commission on Illumination).
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 278-292
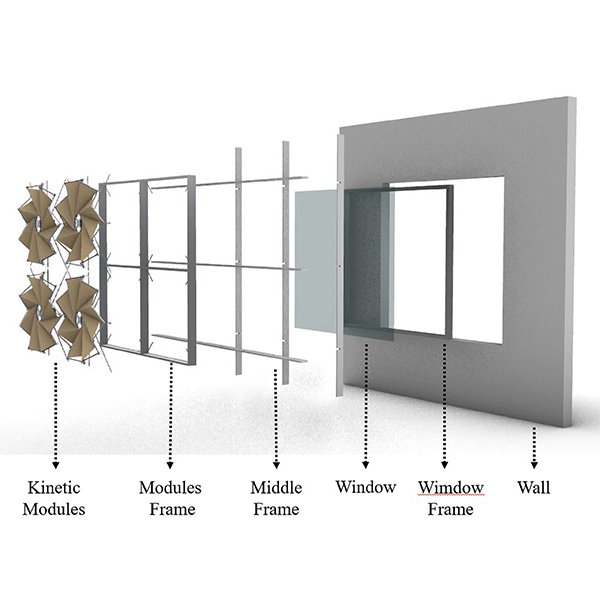
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Designing a Kinetic Façade to Control Glare: Inspiration of
In this study, to control glare in buildings with glass facades, a kinetic facade was designed using a pattern inspired by nature. Accordingly, in this study, due to the essential similarity of buildings with plants regarding the inability to move and location, in the first step, plants and their morphology were examined.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 265-277

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Tessellation-Based Origami-Inspired Movable Façade for Daylighting and
This study emphasizes the importance of daylight performance in interior spaces as a critical factor in achieving global Sustainable Development Goals, including energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and healthy living conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 252-264

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Sensitivity Analysis and Optimization of Facade Design to Improve Daylight
This study examines the daylighting performance of a classroom with bilateral opening typology and an adjacent building on one side. The openings are located on the east and west sides of the classroom, with the adjacent building situated on the west side.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 235-251
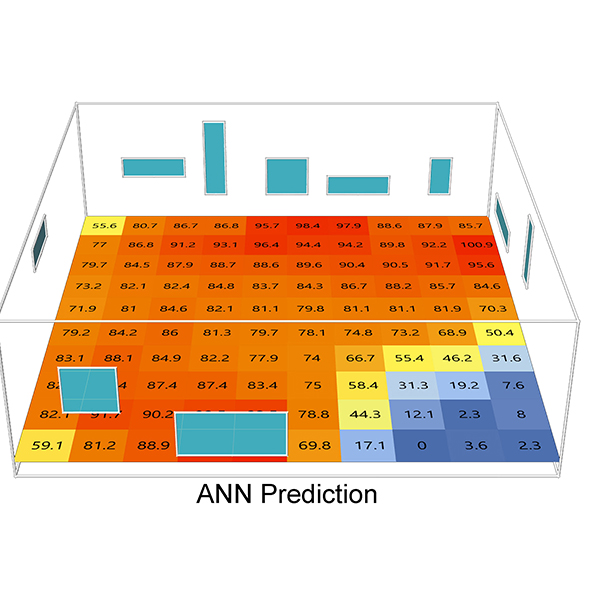
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Unfolding 3D Space into Binary Images for Daylight Simulation via
Daylighting plays a crucial role in building science, impacting both occupants’ well-being and energy consumption in buildings. Balancing the size of openings with energy efficiency has long been a challenge. .
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 204-2013
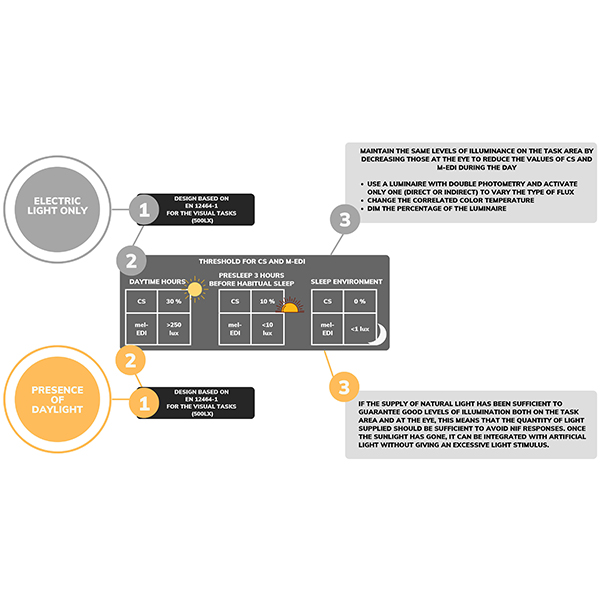
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Integrative Lighting Design: How to Optimize Visual and Non-visual
The objective of this paper is to outline fundamental principles for the electric lighting design of workplace environments such as offices. The study considers both the suggested guidelines and values for non-visual light design and the specifications for visual tasks dictated by the EN 12464-1:2021.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 192-203
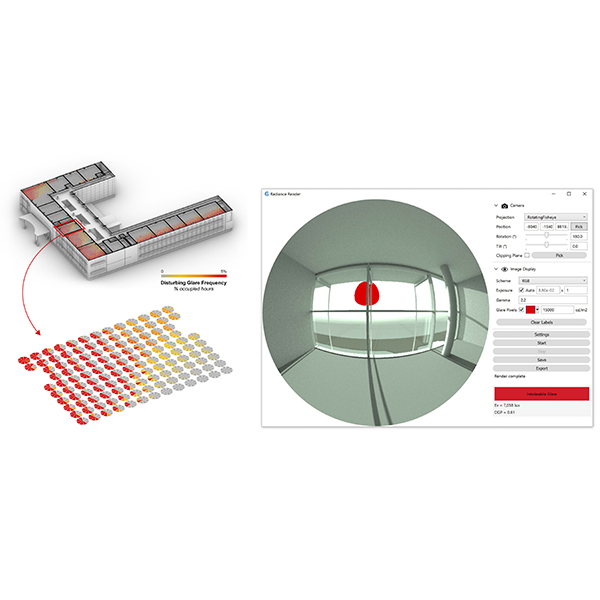
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Parametric Patterned Façade Variations on Daylight
Parametric design influences on building envelope design are exponentially increasing in the current era due to the dominance of computational design on architectural outcomes.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 173-191
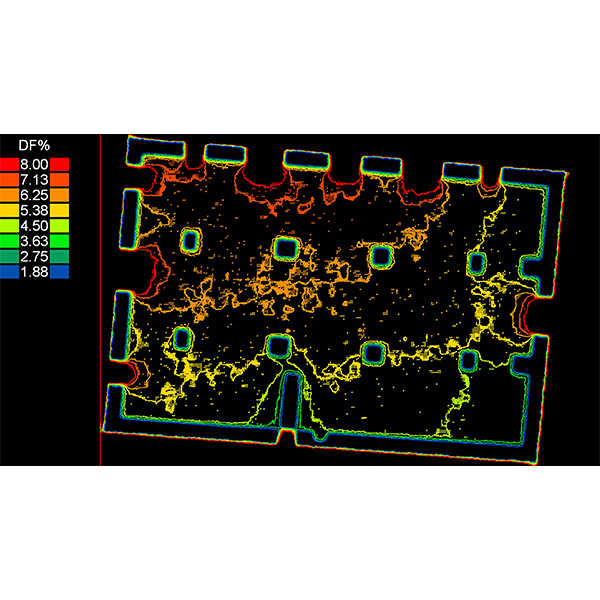
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analysing the Daylighting Performance of the Main Prayer-hall in
This paper studies the daylighting quality of the indoor prayer-hall in The Great Upper Mosque of Hama city in Syria, highlighting this distinctive historical converted building that has been functioning as a mosque since the entry of Islam in the 6th century AD.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 153-172
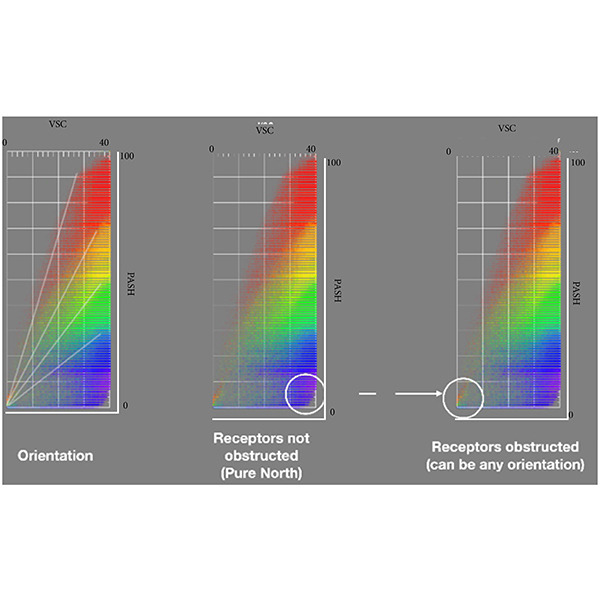
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Sunlight-Daylight Signature: a Novel Concept to Assess Sunlight and
Daylighting and solar availability at urban scale has come to play a crucial role in the perception of discomfort conditions for people, both in outdoor and indoor spaces, and on the energy consumption of buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 136-152
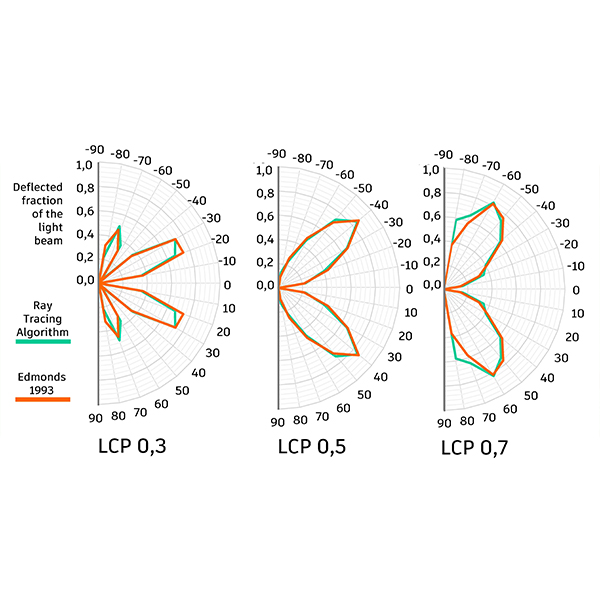
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Ray Tracing Algorithm to Simulate Laser-Cut Panel Light-Redirecting
Daylighting simulation software is an important tool to improve the quality of building design and to improve the quality of the built environment. For its application to correspond to reality, its algorithm needs to reflect real behaviour in the best possible way.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 87-98
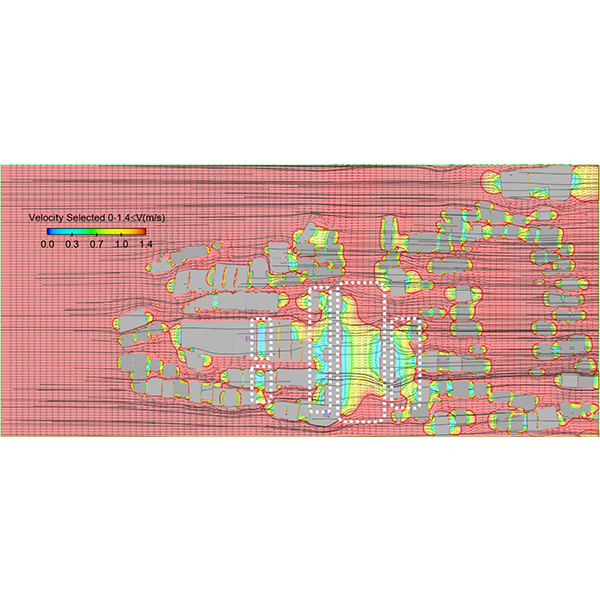
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effects of Orientation and Width of Space Between Buildings
Excessive heat in the high-rise urban fabric has contributed to pedestrian and occupants' discomfort. Establishing wind circulation in space with an environmentally compatible and optimal configuration is necessary to improve comfort in this region.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 99-116
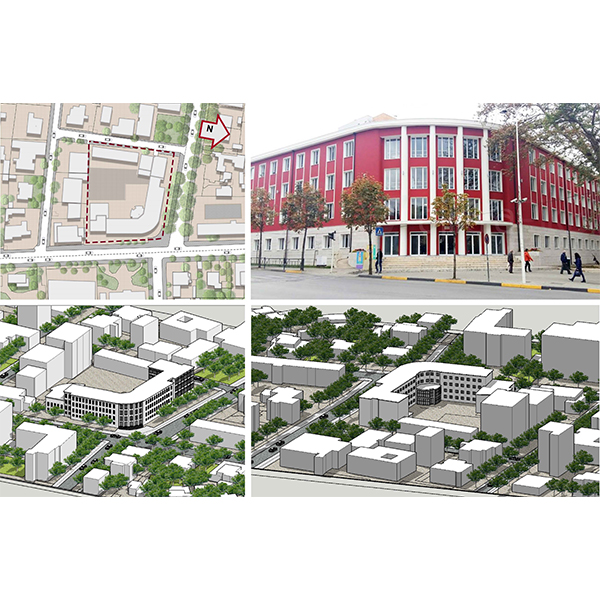

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of the Visual Comfort and Daylight Performance of the
The daylight in classrooms is a crucial aspect that affects the quality of the learning environment and the overall performance of the students. Visual arts, such as painting, sculpture, carving, textile design and photography, require specific lighting conditions, which are different from the regular classroom standards.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 117-135
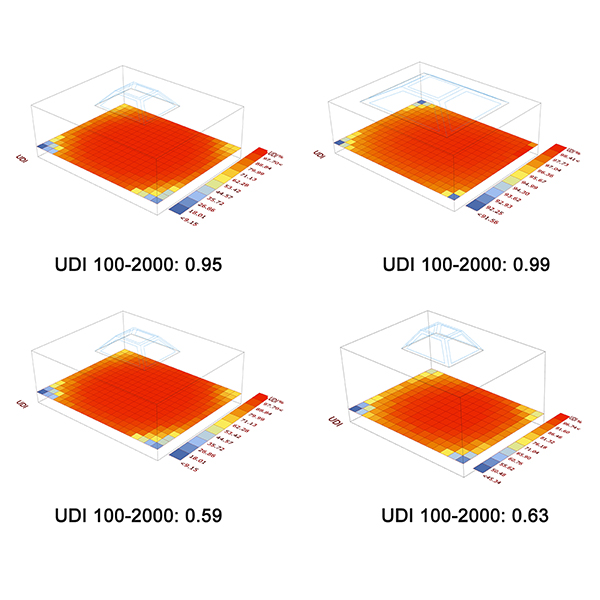
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Optimization of the Skylight for Daylighting and Energy Performance
In terms of sustainable design, lateral windows and skylights are important. Daylighting has become a vital component in office buildings because it increases occupants' productivity, well-being, and energy savings via windows and skylights.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 72-86

RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Architectural Design of Building Façade Models Related to
Lighting control integrated with daylighting is recognized as an important and useful strategy in energy efficient building design. One of the right factors to reduce energy consumption for artificial lighting during the day is the maximum utilization of sunlight.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 60-71

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of Occupants’ Visual Perception in Day Lit Scenes: A
Daylight improves indoor environmental quality, the physical and mental health of occupants, and their efficiency. Research in the area of human-centric lighting that considers the visual and non-visual effects of light on human vision, have focused on examining human visual perception in response to a wide variety of lighting aspects.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 45-59

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Impact of Window Design on Dynamic Daylight Performance in an
Window design affects the building's appearance. Besides, it has a significant impact on daylight performance and the visual comfort of interior spaces.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 31-44

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Visual Comfort Assessment of Hospital Patient Rooms with Climate Responsive
As advanced technologies become prevalent, they are being used more widely in numerous fields. The building sector is not an exception. One of these cutting-edge technologies is responsive facades, which are used in buildings and have an undeniable effect on daylighting.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 17-30

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Biomimicry as an Approach to Improve Daylighting Performance in Office
Biomimicry inspired architects to solve complex design problems and develop adaptive solutions for enhancing the environmental quality. Fields of inspiration include energy efficiency, natural ventilation, daylighting, and structural stability.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 1-16
Join our Editorial Board
CVs should be submitted electronically to jd@solarlits.com.
Editorial Board

Prof. Antonio Manuel Peña García
University of Granada, Spain

Dr. Kacem Gairaa
center for renewable energy development, Algeria

Dr Paola Sansoni
CNR-INO, Italy

Prof. Lambros T. Doulos
Hellenic Open University, Greece

Dr Valerio Roberto Maria LO VERSO
Politecnico di Torino (Polytechnic University of Turin), Italy

Dr Ferdinando Salata
University of Rome, Italy

Dr Canan Kandilli
Usak University, Turkey

Prof Francesco Asdrubali
University of Perugia, Italy

Dr Susana Lagüela López
University of Vigo, Spain

Dr Fabio Peron
IUAV University of Venice, Italy

Prof. Nabil Elminshawy
Port Said University, Egypt

Dr Guiqiang Li
University of Science and Technology of China, China

Prof. Barbara Szybinska Matusiak
NTNU, Norway

Prof. Yuehong Su
University of Nottingham, UK

Prof Umberto Berardi
Politecnico di Bari, Italy

Dr Petar Pejic
University of Niš, Serbia

Alp Tural
Virginia Tech, USA

Dr Doris Abigail Chi Pool
Universidad de las Américas Puebla, Mexico

Dr. Francesca Fragliasso
University of Naples Federico II, Italy

Dr. Francesco Nocera
Department of Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of Catania (ITALY), Italy

Dr jian yao
Ningbo University, China

Dr Mohammed Salah Mayhoub
Al-Azhar University, Egypt

Dr Vincenzo Costanzo
University of Catania, Italy

Dr Karam M. Al-Obaidi
Sheffield Hallam University, UK

Dr Hui Lv
Hubei University of Technology, China

Dr Osama Mohamed Omar
University of Bahrain , Bahrain

Dr Seyed Morteza Hosseini
Aalborg University, Denmark

Wei Wang
Southeast University, 中国

Dr. Feride Şener Yılmaz
Istanbul Technical University, Turkey

Dr Ahmed A. Y. Freewan
Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan
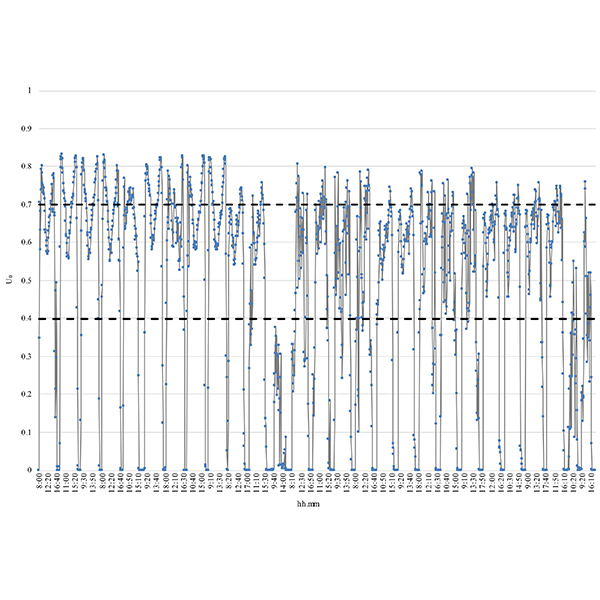
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental Analysis on a 1:2 Scale Model of the
This paper is focused on the daylighting system named Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP) designed by the authors as an evolution of the Double Light Pipe to eliminate the drawbacks due to its encumbrance and the high luminance of its upper portion.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 228-241

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Illumination and Lighting Energy Use in an Office Room with
This paper describes a field study of the illumination and lighting energy use in a full-scale test office in a building located in southern Norway. Natural light is provided to the office via southwest-oriented windows and a horizontal light pipe (HLP) with a daylight entrance facing the south.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 209-227
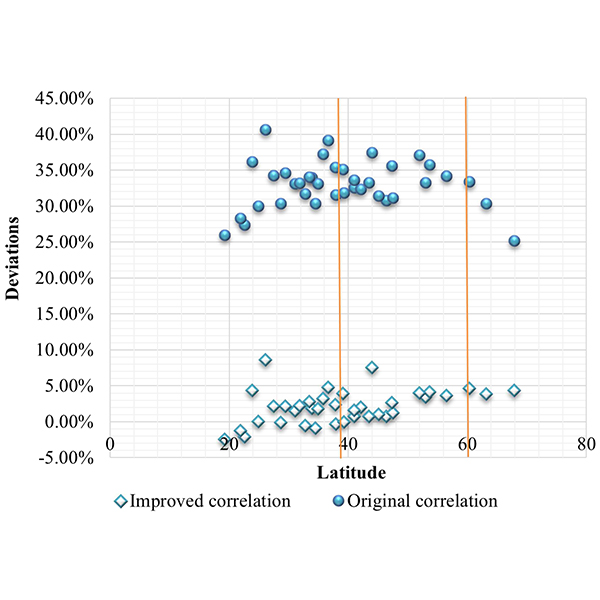
RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Improvement to Calculation of Lighting Energy Requirement in the
Daylighting has a recognized potential for electric energy savings when is used as a complement for artificial lighting. This study reviews the comprehensive calculation method for lighting energy requirement in non-residential buildings introduced by the European Standard EN 15193: 2007 and investigates its feasibility in China.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 16-28
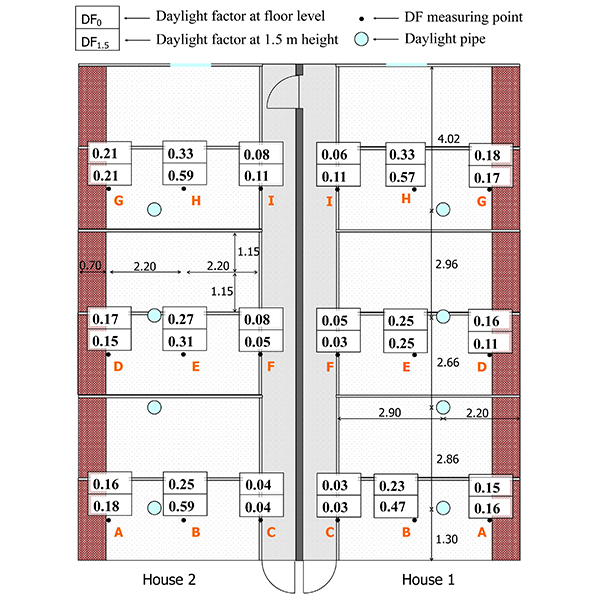
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Lighting Energy Saving with Light Pipe in Farm Animal Production
The Swedish animal production sector has potential for saving electric lighting of €4-9 million per year using efficient daylight utilisation. To demonstrate this, two light pipe systems, Velux® (house 1) and Solatube® (house 2), are installed in two identical pig houses to determine if the required light intensity, daylight autonomy (DA), and reduced electricity use for illumination can be achieved. In.
Journal of Daylighting 2 (2015) 21-31
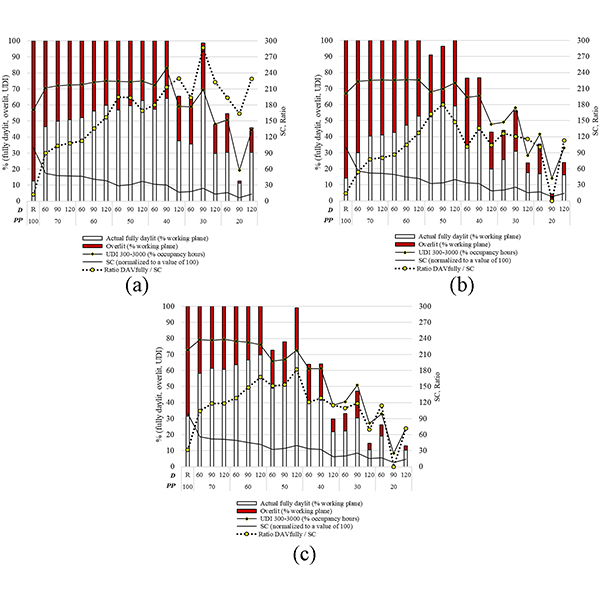
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Perforated Façades for Daylighting and
New design tools have enabled architects to explore complex geometries for building envelopes. Perforated Screens (PS) have gained popularity but their design is still intuitive, often focused on aesthetic and morphological criteria.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 97-111
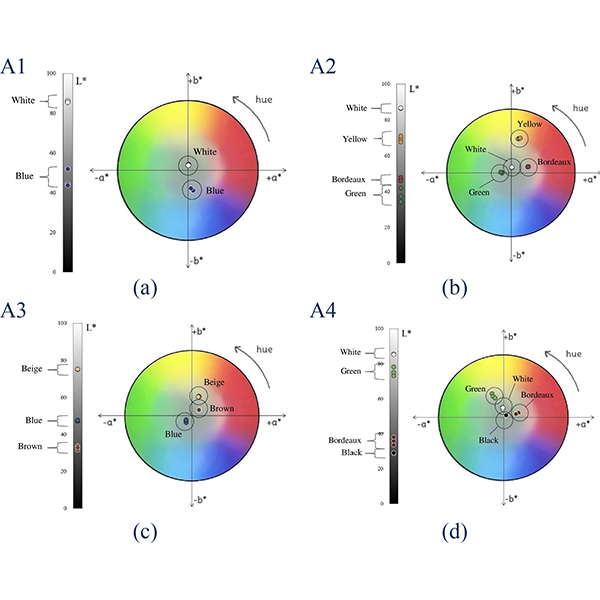
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optical Characteristics of Traditional Portuguese Azulejos: Mixing Colors to Obtain “
The need to reduce energy consumptions in buildings brings modern research to focus on the use of natural sources. In this context, the interest towards traditional architecture has been fueled, since one of the characteristics identifying it is the intuitive and intrinsic link between the building and the surrounding environment.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 273-281
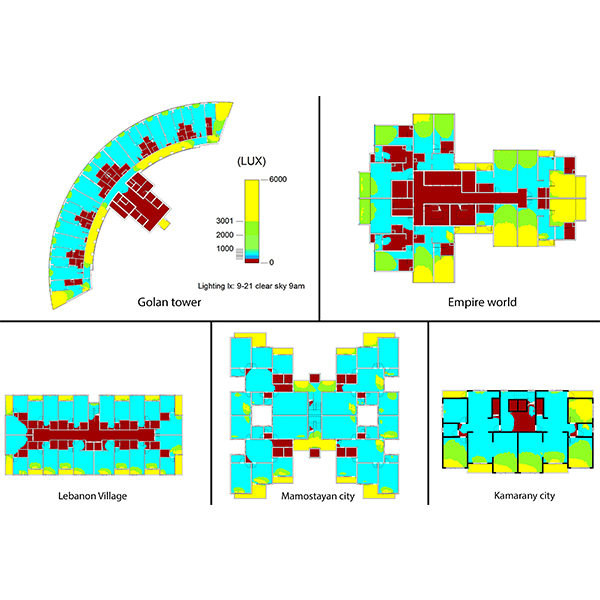
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Impact of Building Typology on Daylight Optimization Using Building Information
Daylight represents one of the crucial factors that affect directly on the building performance and its occupants. This study assesses the daylight performance in the multi-storey residential buildings (apartments) in Erbil city.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 187-201

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Improvement of Daylight Factor Model for Window Size Optimization and
Based on a new approach for the prediction of the Daylight Factor (DF), using existing empirical models, this research work presents an optimization of window size and daylight provided by the glazed apertures component for a building located in a hot and dry climate.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 204-221
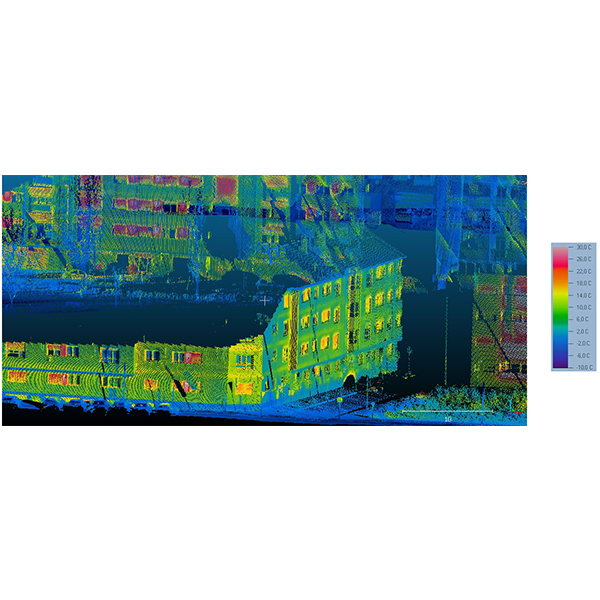
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Thermographic Mobile Mapping of Urban Environment for Lighting and Energy
The generation of 3D models of buildings has been proved as a useful procedure for multiple applications related to energy, from energy rehabilitation management to design of heating systems, analysis of solar contribution to both heating and lighting of buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 8-15
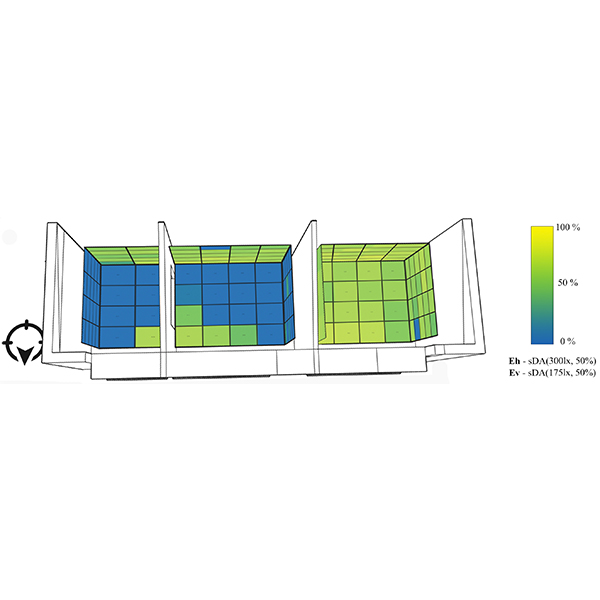
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylighting metrics: an approach to dynamic cubic illuminance
Advances in research work in the field of numerical analysis of daylight performance have generated in-depth knowledge on photometric measurements of daylight quality.
Journal of Daylighting 5 (2018) 34-42
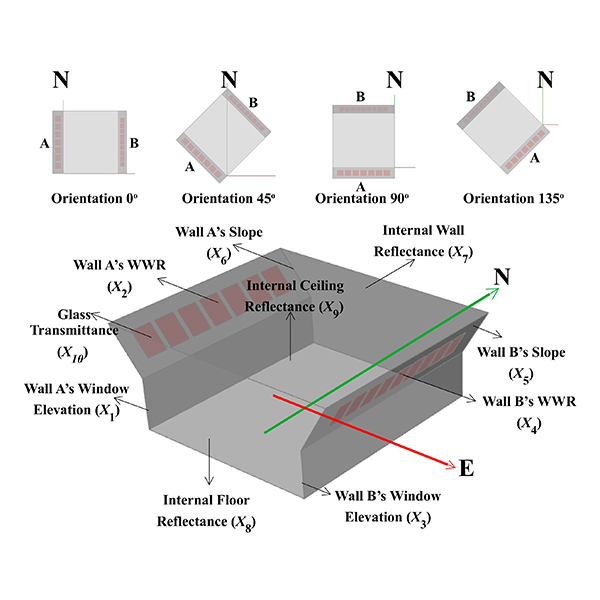
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimization of Daylighting Design Using Self-Shading Mechanism in Tropical
Despite its potential, daylighting strategies in school classrooms in the tropical climate regions is little explored in the literature. The use of two-sided or bilateral daylight opening, as well as the self-shading mechanism using sloped walls, are currently seen as potential strategies to achieve good daylighting in tropical buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 117-136
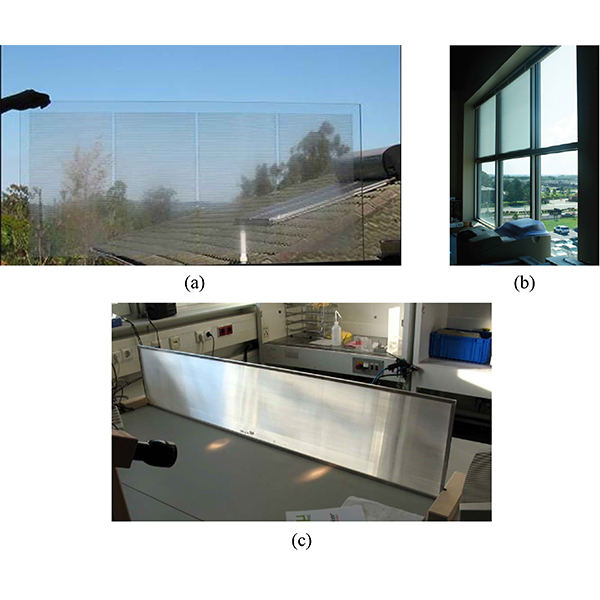
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Annual Performance Assessment of Complex Fenestration Systems in Sunny Climates
Complex Fenestration Systems (CFS) are advanced daylighting systems that are placed on the upper part of a window to improve the indoor daylight distribution within rooms.
Journal of Daylighting 2 (2015) 32-43
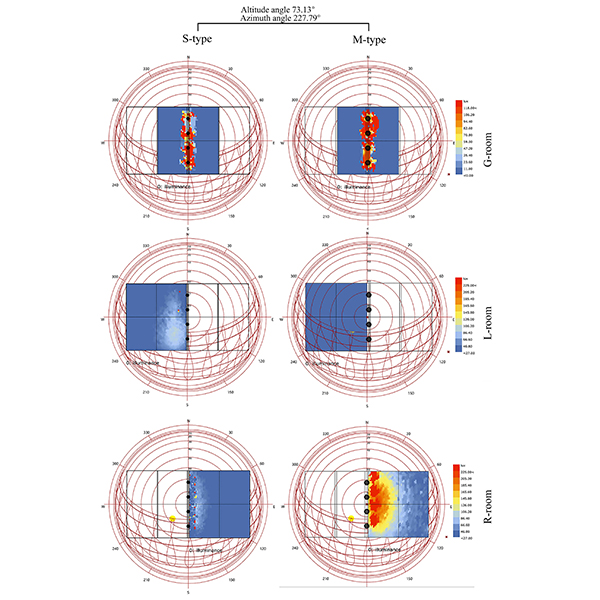
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Novel Approach to Multi-Apertures and Multi-Aspects Ratio
Daylightophil architecture concept is one of the most significant ways to reduce the electrical load consumption in building sector. In deep-plan buildings, or windowless buildings, advanced light transmission systems are used to compensate lighting demands in high-performance architecture theory.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 186-200
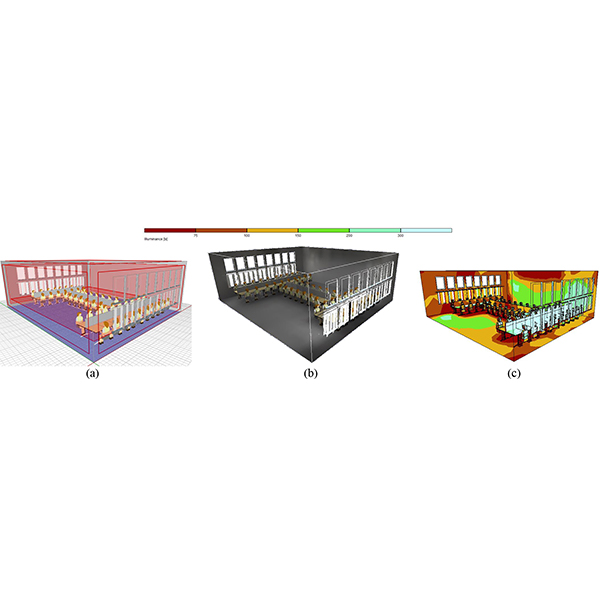
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Analysis of Architectural Elements on Daylight, Visual Comfort, and
The quality of visual comfort has always been an essential element considering human comfort. Providing visual comfort in a living environment reduces the need for artificial lighting, which subsequently has a direct relationship with energy consumptions and its expenses.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 57-72
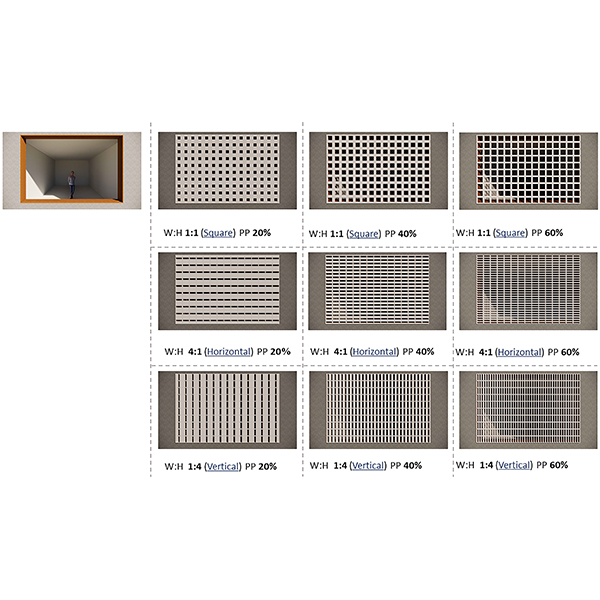
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Significance of Aperture Proportion for the Lighting Behaviour and
Traditional solar screens in Iran (called Moshabak) are architectural devices used mainly in hot-arid regions, with two interrelated functions: controlling the penetration of sunlight and gaze from outside.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 242-256
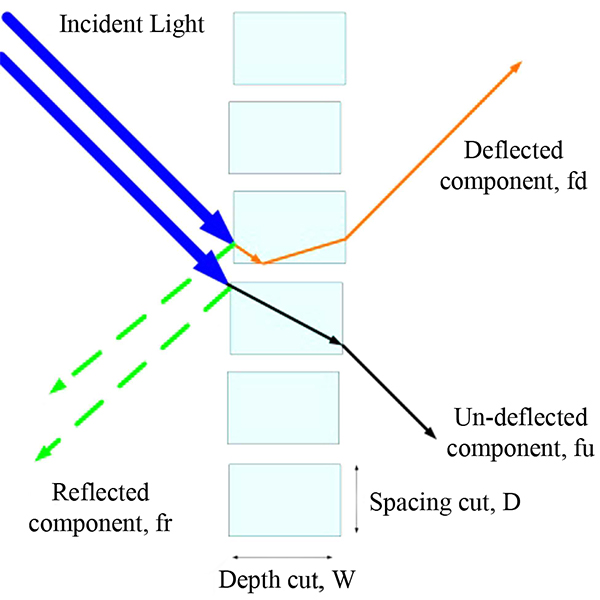
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Maximizing the Performance of Laser Cut Panel by Interaction of
The interaction between different ceiling geometries with laser cut panels (LCPs) is investigated using real experiments and computer simulations to maximize the daylight performance of the LCP.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 29-35
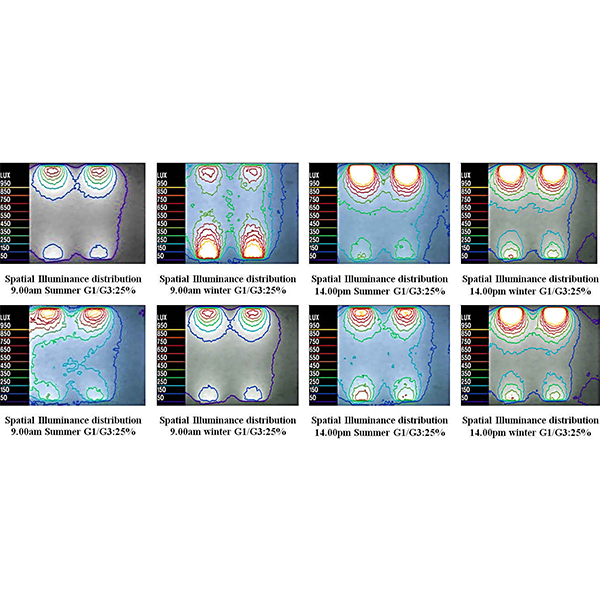
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimum Glazing Configurations for Visual Performance in Algerian Classrooms under
Daylight quality and quantity in Algerian schools show serious problems in ensuring visual comfort of students and teachers. Some problems are due to window design, which leads to excessive amount of sunlight penetration into the classrooms.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 11-22
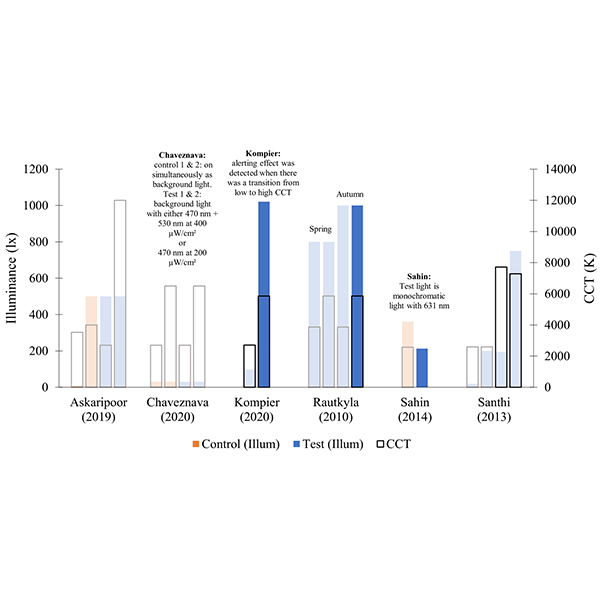
REVIEW ARTICLE
Alerting Effect of Light: A Review of Daytime Studies
Light affects humans beyond only image formation. Several studies have reported that light can increase daytime alertness and can therefore be positively utilized to counter daytime fatigue and increase productivity in workspaces.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 150-163
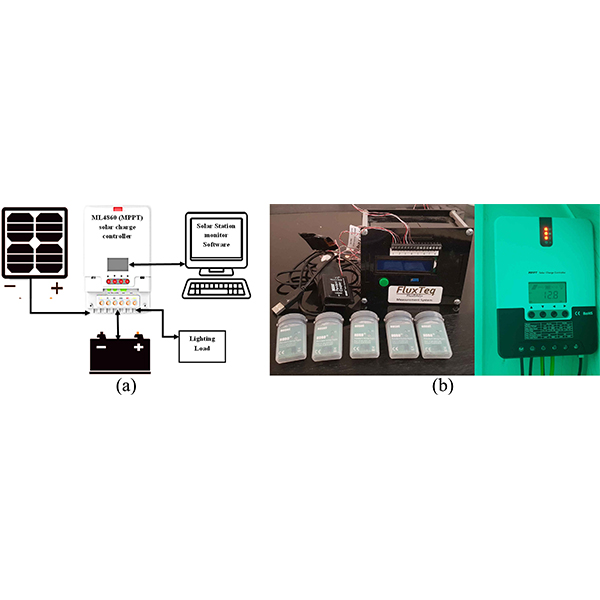
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental Investigation of Overall Energy Performance in Algerian Office Building
Building integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) energy has now become one of the most significant renewable energy alternatives for providing natural daylight and clean energy.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 23-41

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Simulation of Daylighting Conditions in a Virtual Underground City
From the Piranesi fantastic architectures to the animation movies and video games of the last thirty years, a new design approach has been introduced and developed: the design of the virtual space.
Journal of Daylighting 2 (2015) 1-11
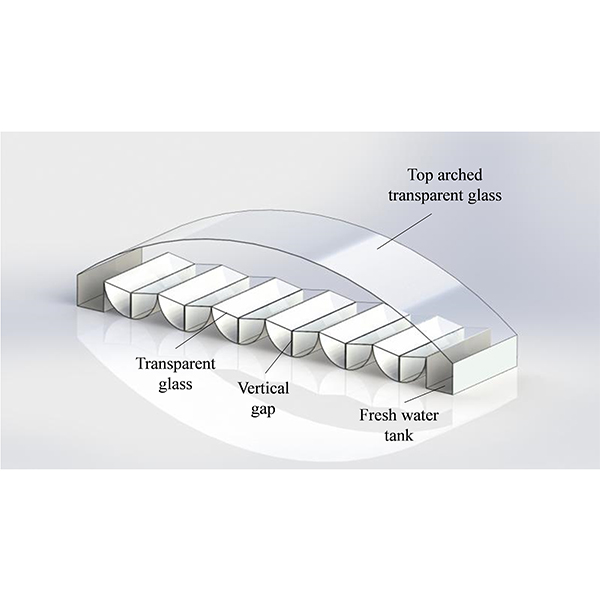
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optical Analysis of a New Solar Distiller with Cylindrical Surface
In this paper, a new solar distiller floating on ocean with cylindrical surface concentrator and vertical gap evaporator is proposed for solving the problem of freshwater shortage in islands.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 100-109
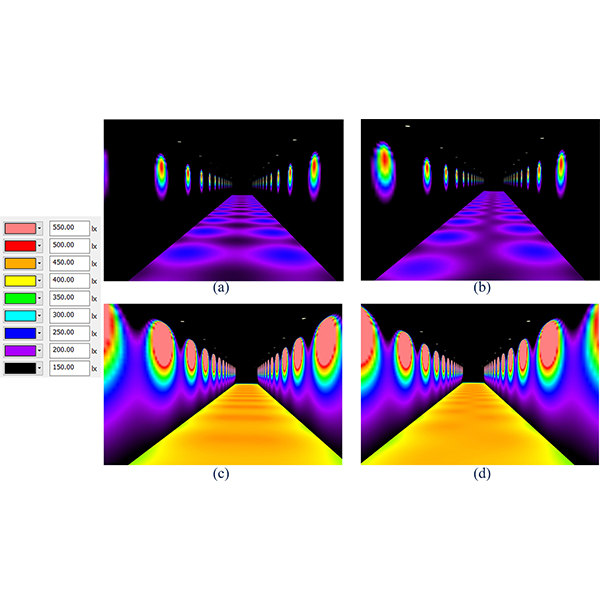
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Phasor Method to Estimate Illuminances Due to Parallel Arrays of
Direct horizontal illuminance along a calculation row due to two parallel arrays of large numbers of identical light sources behaves like a periodic signal with a sinusoidal pattern, which contains useful information for design purpose.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 246-257
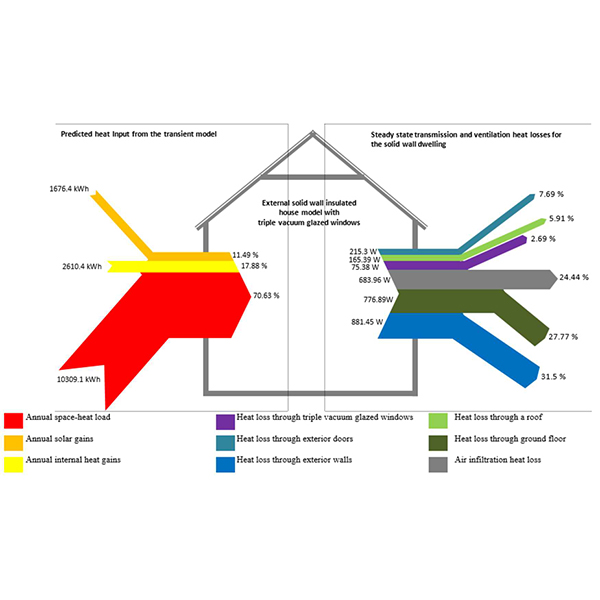
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Solar Energy Gain and Space-Heating Energy Supply Analyses for
A considerable effort is devoted to devising retrofit solutions for reducing space-heating energy in the domestic sector. Existing UK solid-wall dwellings, which have both heritage values and historic fabric, are being improved but yet they tend to have meagre thermal performance, partly, due to the heat-loss through glazings.
Journal of Daylighting 4 (2017) 15-25
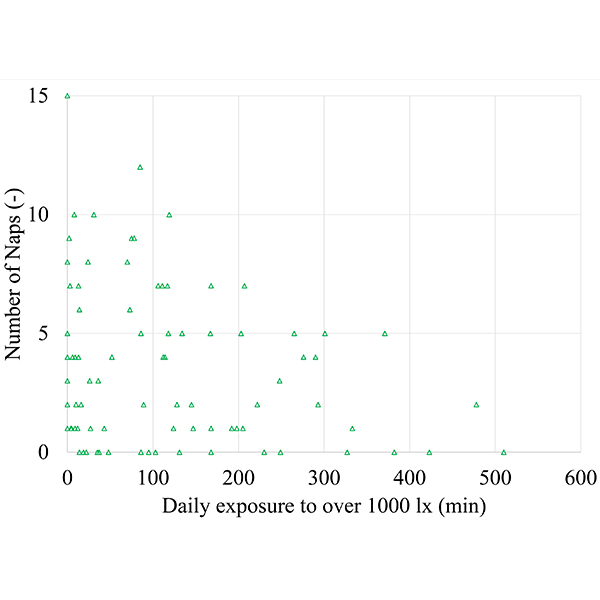
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Exploring the Impact of Natural Light Exposure on Sleep of
Studies among people with dementia demonstrated that the sleep quality and rhythm improves significantly when people are exposed to ambient bright light.
Journal of Daylighting 5 (2018) 14-20
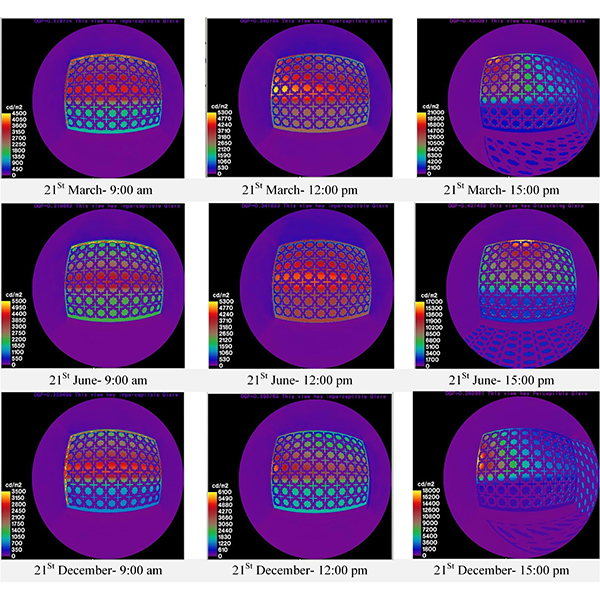
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Role of Orosi’s Islamic Geometric Patterns in the
The form of the building facade significantly affects the amount of useful daylight admitted in the interior space. Striking a balance between the visual comforts of occupants and taking advantage of daylight is always a challenge and, therefore, investigating complex, geometric forms of Orosi patterns can be an effective way of improving visual comfort alongside the aesthetic aspects.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 201-221
 HOME
HOME